Page 482 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 482
APPLICATIONS 8 DEVELOPMENT AND MULTI-FUNCTIONALIZATION OF HIGH-FUNCTIONAL SEPARATION MEMBRANES
-4
-5
-6
-8
-7
-3
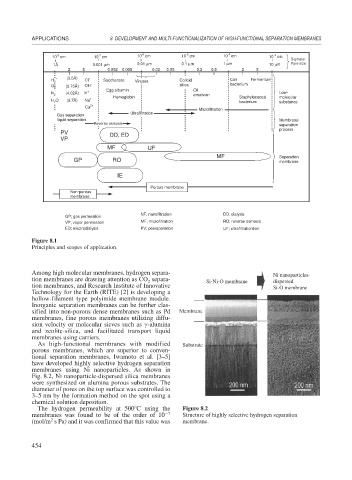
10 cm 10 cm 10 cm 10 cm 10 cm 10 cm
Diameter
1Å 0.001 μm 0.01 μm 0.1 μm 1 μm 10 μm Pore size
2 5 0.002 0.005 0.02 0.05 0.2 0.5 2 5
∗ (3.5Å) −
l
H 2 Cl Saccharose Viruses Colloid Coli Fermentum
− bacterium
O (3.75Å) OH silica
2 Egg albumin Oil
N (4.02Å) H + Low-
2 emulsion
+ Hemoglobin Staphylococcal molecular
H O (3.7Å) Na
2 bacterium substance
2∗
Ca
Microfiltration
Ultrafiltration
Gas separation
liquid separation Membrane
Reverse osmosis separation
Reverse osmosis
process
PV DD, ED
VP
MF UF
MF Separation
GP RO membrane
IE
Porous membrane
Non-porous
membrane
N NF; nanofiltration DD; dialysis
GP; gas permeation
RO; reverse osmosis
VP; vapor permeation M MF; microfiltration RO
PV
E ED; electrodialysis PV; pervaporation UF; ultrafiltrationtion
Figure 8.1
Principles and scopes of application.
Among high molecular membranes, hydrogen separa- Ni nanoparticles-
tion membranes are drawing attention as CO separa- Si-Ni-O membrane dispersed
2
tion membranes, and Research Institute of Innovative Si-O membrane
Technology for the Earth (RITE) [2] is developing a
hollow-filament type polyimide membrane module.
Inorganic separation membranes can be further clas-
sified into non-porous dense membranes such as Pd Membrane
membranes, fine porous membranes utilizing diffu-
sion velocity or molecular sieves such as -alumina
and zeolite-silica, and facilitated transport liquid
membranes using carriers.
As high-functional membranes with modified Substrate
porous membranes, which are superior to conven-
tional separation membranes, Iwamoto et al. [3–5]
have developed highly selective hydrogen separation
membranes using Ni nanoparticles. As shown in
Fig. 8.2, Ni nanoparticle-dispersed silica membranes
were synthesized on alumina porous substrates. The
diameter of pores on the top surface was controlled to
3–5 nm by the formation method on the spot using a
chemical solution deposition.
The hydrogen permeability at 500 C using the Figure 8.2
membranes was found to be of the order of 10 7 Structure of highly selective hydrogen separation
2
(mol/m s Pa) and it was confirmed that this value was membrane.
454