Page 53 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 53
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 1 BASIC PROPERTIES AND MEASURING METHODS OF NANOPARTICLES
Amorphous Tetragonal Monoclinic on silicon and so on. For example, thinner the thick-
ness of the dielectric layer in Multi-Layer Ceramic
Capacitor (MLCC), larger the capacitance of the
resultant MLCC. Deposition of the high-performance
Free Energy on a silicon wafer can lead to the development of various
ΔE
capacitors and the memories of ferroelectric thin films
1
type nanosensors and Micro-Electro-Mechanical
ΔE Systems (MEMS).
ΔG 2 Functionalities such as piezoelectricity and ferro-
electricity of the ferroelectric materials are originated
from domain structure of dipole which forms by the
(a) slight asymmetry of the crystal structure. Therefore,
the crystal structures or the electrical properties of the
ferroelectric thin films are significantly affected by
the substrate and deposition technique which lead to
the difference of the residual stress in films. The
control of the residual stress in the ferroelectric thin
Free Energy actively conducting the related studies on the residual
films is the current topic and many researchers are
stress in ferroelectric thin films.
The most famous ferroelectric materials are the
3
ΔG Smaller Particle size barium titanate (BaTiO ) family as dielectric materi-
als and the lead zirconate titanate (Pb(Zr, Ti)O ) fam-
3
(b) ily as piezoelectric materials. In this section, the size
effects of these two materials are focused to discuss
the crystal structure of the nanoparticles.
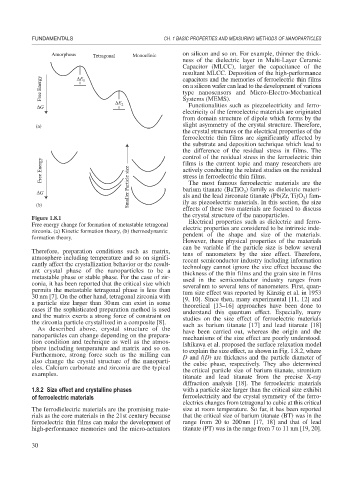
Figure 1.8.1
Free energy change for formation of metastable tetragonal Electrical properties such as dielectric and ferro-
zirconia. (a) Kinetic formation theory, (b) thermodynamic electric properties are considered to be intrinsic inde-
formation theory. pendent of the shape and size of the materials.
However, these physical properties of the materials
can be variable if the particle size is below several
Therefore, preparation conditions such as matrix, tens of nanometers by the size effect. Therefore,
atmosphere including temperature and so on signifi- recent semiconductor industry including information
cantly affect the crystallization behavior or the result- technology cannot ignore the size effect because the
ant crystal phase of the nanoparticles to be a thickness of the thin films and the grain size in films
metastable phase or stable phase. For the case of zir- used in the semiconductor industry ranges from
conia, it has been reported that the critical size which severalnm to several tens of nanometers. First, quan-
permits the metastable tetragonal phase is less than tum size effect was reported by Känzig et al. in 1953
30 nm [7]. On the other hand, tetragonal zirconia with [9, 10]. Since then, many experimental [11, 12] and
a particle size larger than 30nm can exist in some theoretical [13–16] approaches have been done to
cases if the sophisticated preparation method is used understand this quantum effect. Especially, many
and the matrix exerts a strong force of constraint on studies on the size effect of ferroelectric materials
the zirconia particle crystallized in a composite [8]. such as barium titanate [17] and lead titanate [18]
As described above, crystal structure of the have been carried out, whereas the origin and the
nanoparticles can change depending on the prepara- mechanisms of the size effect are poorly understood.
tion condition and technique as well as the atmos- Ishikawa et al. proposed the surface relaxation model
phere including temperature and matrix and so on. to explain the size effect, as shown in Fig. 1.8.2, where
Furthermore, strong force such as the milling can D and l(D) are thickness and the particle diameter of
also change the crystal structure of the nanoparti- the cubic phase, respectively. They also determined
cles. Calcium carbonate and zirconia are the typical the critical particle size of barium titanate, strontium
examples.
titanate and lead titanate from the precise X-ray
diffraction analysis [18]. The ferroelectric materials
1.8.2 Size effect and crystalline phases with a particle size larger than the critical size exhibit
of ferroelectric materials ferroelectricity and the crystal symmetry of the ferro-
electrics changes from tetragonal to cubic at this critical
The ferrodielectric materials are the promising mate- size at room temperature. So far, it has been reported
rials as the core materials in the 21st century because that the critical size of barium titanate (BT) was in the
ferroelectric thin films can make the development of range from 20 to 200nm [17, 18] and that of lead
high-performance memories and the micro-actuators titanate (PT) was in the range from 7 to 11 nm [19, 20].
30