Page 56 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 56
1.9 SURFACE CHARACTERISTICS FUNDAMENTALS
Surface
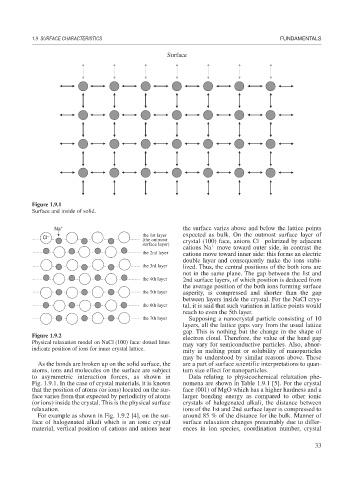
Figure 1.9.1
Surface and inside of solid.
Na + the surface varies above and below the lattice points
Cl − the 1st layer expected as bulk. On the outmost surface layer of
(the outmost crystal (100) face, anions Cl polarized by adjacent
surface layer)
cations Na move toward outer side, in contrast the
the 2nd layer cations move toward inner side: this forms an electric
double layer and consequently make the ions stabi-
the 3rd layer lized. Thus, the central positions of the both ions are
not in the same plane. The gap between the 1st and
the 4th layer 2nd surface layers, of which position is deduced from
the average position of the both ions forming surface
the 5th layer asperity, is compressed and shorter than the gap
between layers inside the crystal. For the NaCl crys-
the 6th layer tal, it is said that such variation in lattice points would
reach to even the 5th layer.
the 7th layer Supposing a nanocrystal particle consisting of 10
layers, all the lattice gaps vary from the usual lattice
gap. This is nothing but the change in the shape of
Figure 1.9.2 electron cloud. Therefore, the value of the band gap
Physical relaxation model on NaCl (100) face: dotted lines may vary for semiconductive particles. Also, abnor-
indicate position of ions for inner crystal lattice.
mity in melting point or solubility of nanoparticles
may be understood by similar reasons above. These
As the bonds are broken up on the solid surface, the are a part of surface scientific interpretations to quan-
atoms, ions and molecules on the surface are subject tum size effect for nanoparticles.
to asymmetric interaction forces, as shown in Data relating to physicochemical relaxation phe-
Fig. 1.9.1. In the case of crystal materials, it is known nomena are shown in Table 1.9.1 [5]. For the crystal
that the position of atoms (or ions) located on the sur- face (001) of MgO which has a higher hardness and a
face varies from that expected by periodicity of atoms larger bonding energy as compared to other ionic
(or ions) inside the crystal. This is the physical surface crystals of halogenated alkali, the distance between
relaxation. ions of the 1st and 2nd surface layer is compressed to
For example as shown in Fig. 1.9.2 [4], on the sur- around 85 % of the distance for the bulk. Manner of
face of halogenated alkali which is an ionic crystal surface relaxation changes presumably due to differ-
material, vertical position of cations and anions near ences in ion species, coordination number, crystal
33