Page 550 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 550
APPLICATIONS 25 DEVELOPMENT OF NEW COSMETICS BASED ON NANOPARTICLES
(a) (b) (c)
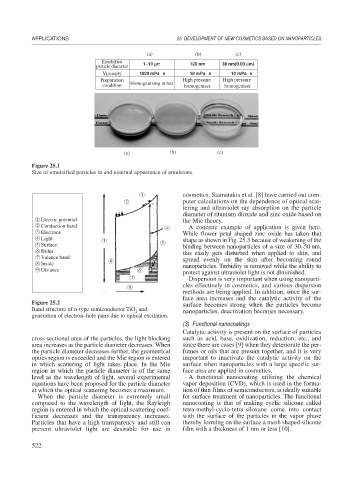
Emulsified 1~10 μm 120 nm 30 nm(0.03 μm)
μ
particle diameter
Viscosity 1020 mPa ⋅ s 18 mPa ⋅ s 10 mPa ⋅ s
Preparation High pressure High pressure
condition Homogenizing mixer homogenizer homogenizer
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 25.1
Size of emulsified particles in and external appearance of emulsions.
3 cosmetics. Stamatakis et al. [8] have carried out com-
2 puter calculations on the dependence of optical scat-
tering and ultraviolet ray absorption on the particle
diameter of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide based on
1 Electric potential the Mie theory.
2 Conduction band
4 A concrete example of application is given here.
3 Electrons While flower petal shaped zinc oxide has taken that
4 Light
1 shape as shown in Fig. 25.3 because of weakening of the
5 Surface 5 binding between nanoparticles of a size of 30–50 nm,
6 Holes this easily gets disturbed when applied to skin, and
7 Valence band
8 spread evenly on the skin after becoming round
8 Inside nanoparticles. Turbidity is removed while the ability to
9 Distance 6 protect against ultraviolet light is not diminished.
7 Dispersion is very important when using nanoparti-
cles effectively in cosmetics, and various dispersion
9
methods are being applied. In addition, since the sur-
face area increases and the catalytic activity of the
Figure 25.2 surface becomes strong when the particles become
Band structure of n-type semiconductor TiO and nanoparticles, deactivation becomes necessary.
2
generation of electron–hole pairs due to optical excitation.
(3) Functional nanocoatings
Catalytic activity is present on the surface of particles
cross-sectional area of the particles, the light blocking such as acid, base, oxidization, reduction, etc., and
area increases as the particle diameter decreases. When since there are cases [9] when they deteriorate the per-
the particle diameter decreases further, the geometrical fumes or oils that are present together, and it is very
optics region is exceeded and the Mie region is entered important to inactivate the catalytic activity on the
in which scattering of light takes place. In the Mie surface when nanoparticles with a large specific sur-
region in which the particle diameter is of the same face area are applied in cosmetics.
level as the wavelength of light, several experimental A functional nanocoating utilizing the chemical
equations have been proposed for the particle diameter vapor deposition (CVD), which is used in the forma-
at which the optical scattering becomes a maximum. tion of thin films of semiconductors, is ideally suitable
When the particle diameter is extremely small for surface treatment of nanoparticles. The functional
compared to the wavelength of light, the Rayleigh nanocoating is that of making cyclic silicone called
region is entered in which the optical scattering coef- tetra-methyl-cyclo-tetra-siloxane come into contact
ficient decreases and the transparency increases. with the surface of the particles in the vapor phase
Particles that have a high transparency and still can thereby forming on the surface a mesh shaped silicone
prevent ultraviolet light are desirable for use in film with a thickness of 1 nm or less [10].
522