Page 545 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 545
24 CLOSELY PACKED COLLOIDAL CRYSTAL APPLICATIONS
edge surrounding the substrate. The colloidal crystal 2. Structural color of colloidal crystal and its tuning
film indicates the mono structural color of green mechanism
without the play of color phenomena.
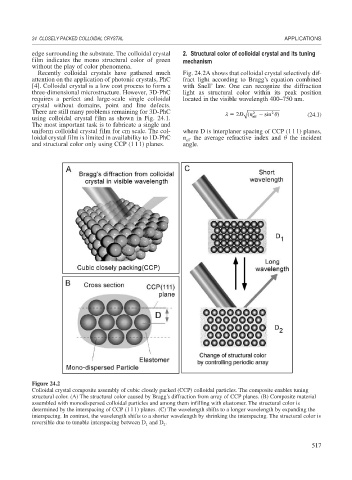
Recently colloidal crystals have gathered much Fig. 24.2A shows that colloidal crystal selectively dif-
attention on the application of photonic crystals, PhC fract light according to Bragg’s equation combined
[4]. Colloidal crystal is a low cost process to form a with Snell’ law. One can recognize the diffraction
three-dimensional microstructure. However, 3D-PhC light as structural color within its peak position
requires a perfect and large-scale single colloidal located in the visible wavelength 400–750 nm.
crystal without domains, point and line defects.
There are still many problems remaining for 3D-PhC 2D ( n 2 sin 2 ) (24.1)
using colloidal crystal film as shown in Fig. 24.1. eff
The most important task is to fabricate a single and
uniform colloidal crystal film for cm scale. The col- where D is interplaner spacing of CCP (111) planes,
loidal crystal film is limited in availability to 1D-PhC n eff the average refractive index and the incident
and structural color only using CCP (111) planes. angle.
Figure 24.2
Colloidal crystal composite assembly of cubic closely packed (CCP) colloidal particles. The composite enables tuning
structural color. (A) The structural color caused by Bragg’s diffraction from array of CCP planes. (B) Composite material
assembled with monodispersed colloidal particles and among them infilling with elastomer. The structural color is
determined by the interspacing of CCP (111) planes. (C) The wavelength shifts to a longer wavelength by expanding the
interspacing. In contrast, the wavelength shifts to a shorter wavelength by shrinking the interspacing. The structural color is
reversible due to tunable interspacing between D and D .
2
1
517