Page 546 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 546
APPLICATIONS 24 CLOSELY PACKED COLLOIDAL CRYSTAL
The structural color can be changed by tuning inter- colloidal particle and PDMS elastomer cause the
planer spacing, D, or changing the average refractive tuning of the interplaner spacing of CCP (111) planes
index, n . In earlier work, structural color was and the structural color of the composite.
eff
changed by n . Stein et al. reported colorful struc-
eff
tural color of PhC pigments infilling with solvents or 3. Tunable structural color by swelling with liquid
polymer having different reflex index [5]. Recent
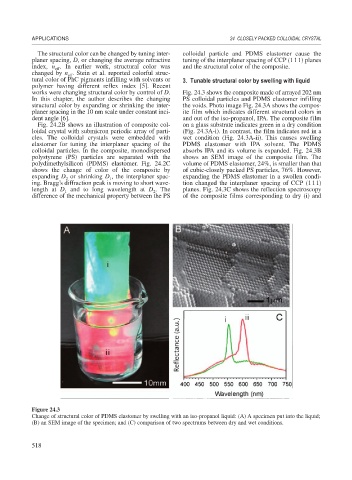
works were changing structural color by control of D. Fig. 24.3 shows the composite made of arrayed 202 nm
In this chapter, the author describes the changing PS colloidal particles and PDMS elastomer infilling
structural color by expanding or shrinking the inter- the voids. Photo image Fig. 24.3A shows the compos-
planer spacing in the 10 nm scale under constant inci- ite film which indicates different structural colors in
dent angle [6]. and out of the iso-propanol, IPA. The composite film
Fig. 24.2B shows an illustration of composite col- on a glass substrate indicates green in a dry condition
loidal crystal with submicron periodic array of parti- (Fig. 24.3A-i). In contrast, the film indicates red in a
cles. The colloidal crystals were embedded with wet condition (Fig. 24.3A-ii). This causes swelling
elastomer for tuning the interplaner spacing of the PDMS elastomer with IPA solvent. The PDMS
colloidal particles. In the composite, monodispersed absorbs IPA and its volume is expanded. Fig. 24.3B
polystyrene (PS) particles are separated with the shows an SEM image of the composite film. The
polydimethylsilicon (PDMS) elastomer. Fig. 24.2C volume of PDMS elastomer, 24%, is smaller than that
shows the change of color of the composite by of cubic-closely packed PS particles, 76%. However,
expanding D or shrinking D , the interplaner spac- expanding the PDMS elastomer in a swollen condi-
1
2
ing. Bragg’s diffraction peak is moving to short wave- tion changed the interplaner spacing of CCP (111)
length at D and to long wavelength at D . The planes. Fig. 24.3C shows the reflection spectroscopy
1
2
difference of the mechanical property between the PS of the composite films corresponding to dry (i) and
Figure 24.3
Change of structural color of PDMS elastomer by swelling with an iso-propanol liquid: (A) A specimen put into the liquid;
(B) an SEM image of the specimen; and (C) comparison of two spectrums between dry and wet conditions.
518