Page 23 - Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB and Excel
P. 23
Chapter 1 Introduction to MATLAB
R 1
A
R 2
C
V L
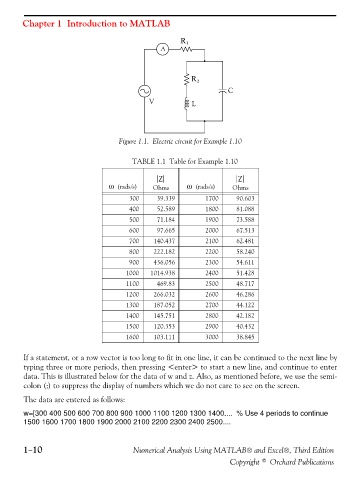
Figure 1.1. Electric circuit for Example 1.10
TABLE 1.1 Table for Example 1.10
Z Z
ω (rads/s) Ohms ω (rads/s) Ohms
300 39.339 1700 90.603
400 52.589 1800 81.088
500 71.184 1900 73.588
600 97.665 2000 67.513
700 140.437 2100 62.481
800 222.182 2200 58.240
900 436.056 2300 54.611
1000 1014.938 2400 51.428
1100 469.83 2500 48.717
1200 266.032 2600 46.286
1300 187.052 2700 44.122
1400 145.751 2800 42.182
1500 120.353 2900 40.432
1600 103.111 3000 38.845
If a statement, or a row vector is too long to fit in one line, it can be continued to the next line by
typing three or more periods, then pressing <enter> to start a new line, and continue to enter
data. This is illustrated below for the data of w and z. Also, as mentioned before, we use the semi-
colon (;) to suppress the display of numbers which we do not care to see on the screen.
The data are entered as follows:
w=[300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400.... % Use 4 periods to continue
1500 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 2100 2200 2300 2400 2500....
1−10 Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB® and Excel®, Third Edition
Copyright © Orchard Publications