Page 460 - Offshore Electrical Engineering Manual
P. 460
Determining Safety Integrity Levels – Process 447
The SIL assessment meeting should consist of a chairperson usually qualified and
experienced in a safety-related discipline and representatives from design, maintenance
and operations. To save time, the software should be preprogrammed with component
failure data, but the sources of this data should be reviewed and agreed during the meeting.
DETERMINING SAFETY INTEGRITY LEVELS – PROCESS
When a process hazards analysis determines that an SIS is required, the level of risk
reduction afforded by the SIS and the target SIL has to be assigned. The effectiveness of
an SIS is described in terms of ‘the probability it will fail to perform its required func-
tion when it is called upon to do so’. This is its probability of failure on demand (PFD).
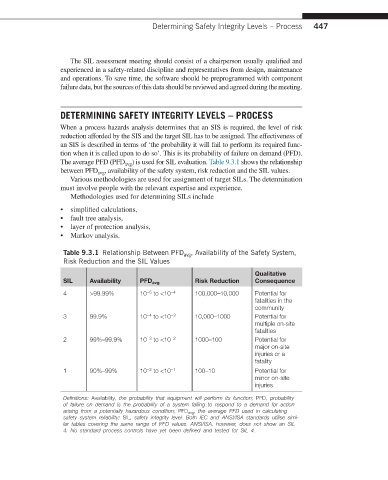
The average PFD (PFD ) is used for SIL evaluation. Table 9.3.1 shows the relationship
avg
between PFD , availability of the safety system, risk reduction and the SIL values.
avg
Various methodologies are used for assignment of target SILs. The determination
must involve people with the relevant expertise and experience.
Methodologies used for determining SILs include
• simplified calculations,
• fault tree analysis,
• layer of protection analysis,
• Markov analysis.
Table 9.3.1 Relationship Between PFD avg , Availability of the Safety System,
Risk Reduction and the SIL Values
Qualitative
SIL Availability PFD avg Risk Reduction Consequence
4 >99.99% 10 to <10 −4 100,000–10,000 Potential for
−5
fatalities in the
community
3 99.9% 10 to <10 −3 10,000–1000 Potential for
−4
multiple on-site
fatalities
−3
2 99%–99.9% 10 to <10 −2 1000–100 Potential for
major on-site
injuries or a
fatality
1 90%–99% 10 to <10 −1 100–10 Potential for
−2
minor on-site
injuries
Definitions: Availability, the probability that equipment will perform its function; PFD, probability
of failure on demand is the probability of a system failing to respond to a demand for action
arising from a potentially hazardous condition; PFD avg , the average PFD used in calculating
safety system reliability; SIL, safety integrity level. Both IEC and ANSI/ISA standards utilise simi-
lar tables covering the same range of PFD values. ANSI/ISA, however, does not show an SIL
4. No standard process controls have yet been defined and tested for SIL 4.