Page 30 - Op Amps Design, Applications, and Troubleshooting
P. 30
Basic Characteristics of Ideal Op Amps 13
2. Combine the individual voltages or currents at the point(s) of interest to
determine the net effect of the multiple sources.
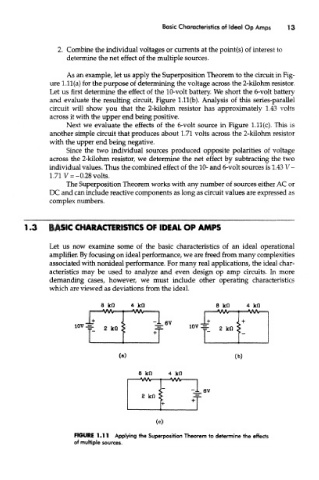
As an example, let us apply the Superposition Theorem to the circuit in Fig-
ure 1.11 (a) for the purpose of determining the voltage across the 2-kilohm resistor.
Let us first determine the effect of the 10-volt battery. We short the 6-volt battery
and evaluate the resulting circuit, Figure l.ll(b). Analysis of this series-parallel
circuit will show you that the 2-kilohm resistor has approximately 1,43 volts
across it with the upper end being positive.
Next we evaluate the effects of the 6-volt source in Figure l.ll(c). This is
another simple circuit that produces about 1.71 volts across the 2-kilohm resistor
with the upper end being negative.
Since the two individual sources produced opposite polarities of voltage
across the 2-kilohm resistor, we determine the net effect by subtracting the two
individual values. Thus the combined effect of the 10- and 6-volt sources is 1.43 V -
1.71 V = -0.28 volts.
The Superposition Theorem works with any number of sources either AC or
DC and can include reactive components as long as circuit values are expressed as
complex numbers.
1.3 BASIC CHARACTERISTICS OF IDEAL OP AMPS
Let us now examine some of the basic characteristics of an ideal operational
amplifier. By focusing on ideal performance, we are freed from many complexities
associated with nonideal performance. For many real applications, the ideal char-
acteristics may be used to analyze and even design op amp circuits. In more
demanding cases, however, we must include other operating characteristics
which are viewed as deviations from the ideal.
FIGURE 1.11 Applying the Superposition Theorem to determine the effects
of multiple sources.