Page 163 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 163
Passive Optical Components
Passive Optical Components 153
TABLE 9.4. Typical Parameter Values of Commercially Available Circulators
Parameter Unit Value
Wavelength band nm C-band: 1525–1565
L-band: 1570–1610
Insertion loss dB 0.6
Channel isolation dB 40
Optical return loss dB 50
Operating power mW 500
Polarization-dependent loss dB 0.1
Polarization mode dispersion ps 0.1
Size (diameter length) mm 5.5 50
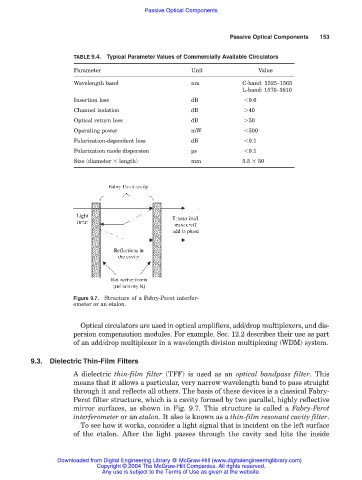
Figure 9.7. Structure of a Fabry-Perot interfer-
ometer or an etalon.
Optical circulators are used in optical amplifiers, add/drop multiplexers, and dis-
persion compensation modules. For example, Sec. 12.2 describes their use as part
of an add/drop multiplexer in a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) system.
9.3. Dielectric Thin-Film Filters
A dielectric thin-film filter (TFF) is used as an optical bandpass filter. This
means that it allows a particular, very narrow wavelength band to pass straight
through it and reflects all others. The basis of these devices is a classical Fabry-
Perot filter structure, which is a cavity formed by two parallel, highly reflective
mirror surfaces, as shown in Fig. 9.7. This structure is called a Fabry-Perot
interferometer or an etalon. It also is known as a thin-film resonant cavity filter.
To see how it works, consider a light signal that is incident on the left surface
of the etalon. After the light passes through the cavity and hits the inside
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.