Page 56 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 56
Optical Components Based on Dynamic Liquid-Liquid Interfaces 37
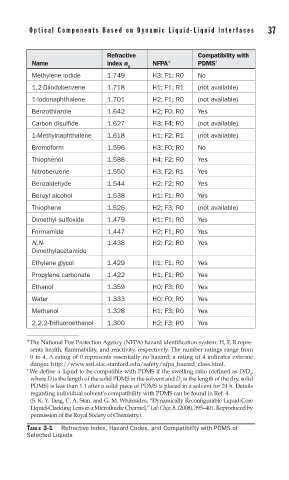
Refractive Compatibility with
Name index n NFPA ∗ PDMS †
d
Methylene iodide 1.749 H3; F1; R0 No
1,2-Diiodobenzene 1.718 H1; F1; R1 (not available)
1-Iodonaphthalene 1.701 H2; F1; R0 (not available)
Benzothiazole 1.642 H2; F0; R0 Yes
Carbon disulfide 1.627 H3; F4; R0 (not available)
1-Methylnaphthalene 1.618 H1; F2; R1 (not available)
Bromoform 1.596 H3; F0; R0 No
Thiophenol 1.588 H4; F2; R0 Yes
Nitrobenzene 1.550 H3; F2; R1 Yes
Benzaldehyde 1.544 H2; F2; R0 Yes
Benzyl alcohol 1.538 H1; F1; R0 Yes
Thiophene 1.526 H2; F3; R0 (not available)
Dimethyl sulfoxide 1.479 H1; F1; R0 Yes
Formamide 1.447 H2; F1; R0 Yes
N,N- 1.438 H2; F2; R0 Yes
Dimethylacetamide
Ethylene glycol 1.429 H1; F1; R0 Yes
Propylene carbonate 1.422 H1; F1; R0 Yes
Ethanol 1.359 H0; F3; R0 Yes
Water 1.333 H0; F0; R0 Yes
Methanol 1.328 H1; F3; R0 Yes
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol 1.300 H2; F3; R0 Yes
∗ The National Fire Protection Agency (NFPA) hazard identification system: H, F, R repre-
sents health, flammability, and reactivity, respectively. The number ratings range from
0 to 4. A rating of 0 represents essentially no hazard; a rating of 4 indicates extreme
danger. http://www.ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/safety/nfpa_hazard_class.html.
† We define a liquid to be compatible with PDMS if the swelling ratio (defined as D/D ,
0
where D is the length of the solid PDMS in the solvent and D is the length of the dry, solid
0
PDMS) is less than 1.1 after a solid piece of PDMS is placed in a solvent for 24 h. Details
regarding individual solvent’s compatibility with PDMS can be found in Ref. 4.
(S. K. Y. Tang, C. A. Stan, and G. M. Whitesides, “Dynamically Reconfigurable Liquid-Core
Liquid-Cladding Lens in a Microfluidic Channel,” Lab Chip, 8, (2008), 395–401. Reproduced by
permission of the Royal Society of Chemistry.)
TABLE 3-1 Refractive Index, Hazard Codes, and Compatibility with PDMS of
Selected Liquids