Page 57 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 57
38 Cha pte r T h ree
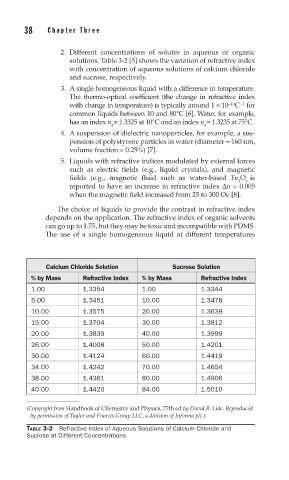
2. Different concentrations of solutes in aqueous or organic
solutions. Table 3-2 [5] shows the variation of refractive index
with concentration of aqueous solutions of calcium chloride
and sucrose, respectively.
3. A single homogeneous liquid with a difference in temperature.
The thermo-optical coefficient (the change in refractive index
with change in temperature) is typically around 1 × 10 °C for
−1
−4
common liquids between 10 and 80°C [6]. Water, for example,
has an index n = 1.3325 at 10°C and an index n = 1.3235 at 75°C.
d d
4. A suspension of dielectric nanoparticles, for example, a sus-
pension of polystyrene particles in water (diameter = 160 nm,
volume fraction = 0.25%) [7].
5. Liquids with refractive indices modulated by external forces
such as electric fields (e.g., liquid crystals), and magnetic
fields (e.g., magnetic fluid such as water-based Fe O is
3 4
reported to have an increase in refractive index Δn = 0.005
when the magnetic field increased from 25 to 300 Oe [8].
The choice of liquids to provide the contrast in refractive index
depends on the application. The refractive index of organic solvents
can go up to 1.75, but they may be toxic and incompatible with PDMS.
The use of a single homogeneous liquid at different temperatures
Calcium Chloride Solution Sucrose Solution
% by Mass Refractive Index % by Mass Refractive Index
1.00 1.3354 1.00 1.3344
5.00 1.3451 10.00 1.3478
10.00 1.3575 20.00 1.3639
15.00 1.3704 30.00 1.3812
20.00 1.3839 40.00 1.3999
26.00 1.4008 50.00 1.4201
30.00 1.4124 60.00 1.4419
34.00 1.4242 70.00 1.4654
38.00 1.4361 80.00 1.4906
40.00 1.4420 84.00 1.5010
(Copyright from Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 77th ed by David R. Lide. Reproduced
by permission of Taylor and Francis Group LLC, a division of Informa plc.)
TABLE 3-2 Refractive Index of Aqueous Solutions of Calcium Chloride and
Sucrose at Different Concentrations