Page 242 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 242
An Intr oduction to Or ganic Photodetectors 219
= RC ln 9 Δt = RC ln 9
Δt r f
1 C
90%
Normalized photovoltage 0.6 R L
0.8
0.4
0.2 Excitation pulse
10%
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Time (AU)
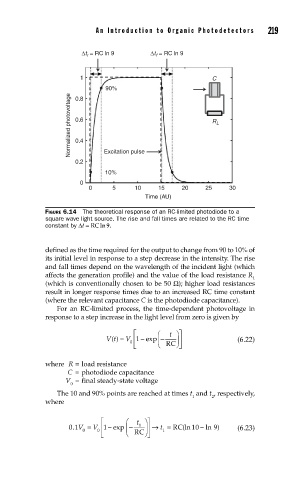
FIGURE 6.14 The theoretical response of an RC-limited photodiode to a
square wave light source. The rise and fall times are related to the RC time
constant by Δt = RCln 9.
defined as the time required for the output to change from 90 to 10% of
its initial level in response to a step decrease in the intensity. The rise
and fall times depend on the wavelength of the incident light (which
affects the generation profile) and the value of the load resistance R
L
(which is conventionally chosen to be 50 Ω); higher load resistances
result in longer response times due to an increased RC time constant
(where the relevant capacitance C is the photodiode capacitance).
For an RC-limited process, the time-dependent photovoltage in
response to a step increase in the light level from zero is given by
⎡ ⎛ t ⎞⎤
Vt() = V ⎢ 1 − exp − ⎟⎥ (6.22)
⎜
0 ⎠
⎣ ⎝ RC ⎦
where R = load resistance
C = photodiode capacitance
V = final steady-state voltage
0
The 10 and 90% points are reached at times t and t , respectively,
1 2
where
⎡ ⎛ t ⎞⎤
−
−
01V = V 0 ⎢ 1 exp − 1 ⎥ → t = RC (ln 10 − ln ) (6.23)
9
.
0 ⎜ ⎟ 1
⎣ ⎢ ⎝ RC ⎠ ⎥ ⎦