Page 48 - Orlicky's Material Requirements Planning
P. 48
CHAPTER 3 The Four Critical Questions Answered 29
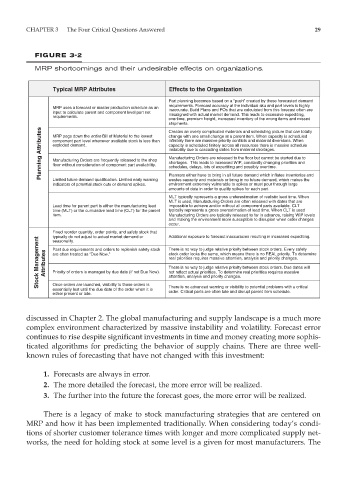
FIGURE 3-2
MRP shortcomings and their undesirable effects on organizations.
Typical MRP Attributes Effects to the Organization
Part planning becomes based on a “push” created by these forecasted demand
requirements. Forecast accuracy at the individual sku and part levels is highly
MRP uses a forecast or master production schedule as an inaccurate. Build Plans and POs that are calculated from this forecast often are
input to calculate parent and component level part net misaligned with actual market demand. This leads to excessive expediting,
requirements.
overtime, premium freight, increased inventory of the wrong items and missed
shipments.
Planning Attributes component part level whenever available stock is less than infinitely there are massive priority conflicts and material diversions. When
Creates an overly complicated materials and scheduling picture that can totally
change with one small change at a parent item. When capacity is scheduled
MRP pegs down the entire Bill of Material to the lowest
exploded demand.
capacity is scheduled finitely across all resources there is massive schedule
instability due to cascading slides from material shortages.
Manufacturing Orders are released to the floor but cannot be started due to
Manufacturing Orders are frequently released to the shop
shortages. This leads to increased WIP, constantly changing priorities and
floor without consideration of component part availability.
schedules, delays, lots of expediting and possibly overtime.
Limited future demand qualification. Limited early warning
wastes capacity and materials or bring in no future demand, which makes the
environment extremely vulnerable to spikes or must pour through large
indicators of potential stock outs or demand spikes. Planners either have to bring in all future demand which inflates inventories and
amounts of data in order to qualify spikes for each part.
MLT typically represents a gross underestimation of realistic lead time. When
MLT is used, Manufacturing Orders are often released with dates that are
Lead time for parent part is either the manufacturing lead impossible to achieve and/or without all component parts available. CLT
time (MLT) or the cumulative lead time (CLT) for the parent typically represents a gross overestimation of lead time. When CLT is used
item. Manufacturing Orders are typically released to far in advance, raising WIP levels
and making the environment more susceptible to disrupion when order changes
occur.
Fixed reorder quantity, order points, and safety stock that Additional exposure to forecast inaccuracies resulting in increased expediting.
typically do not adjust to actual market demand or
Stock Management Attributes Past due requirements and orders to replenish safety stock There is no way to judge relative priority between stock orders. Every safety
seasonality.
are often treated as “Due Now.”
stock order looks the same, which means there is no REAL priority. To determine
real priorities requires massive attention, analysis and priority changes.
There is no way to judge relative priority between stock orders. Due dates will
not reflect actual priorities. To determine real priorities requires massive
Priority of orders is managed by due date (if not Due Now).
Once orders are launched, visibility to those orders is
There is no advanced warning or visibility to potential problems with a critical
essentially lost until the due date of the order when it is attention, analysis and priority changes.
order. Critical parts are often late and disrupt parent item schedule.
either present or late.
discussed in Chapter 2. The global manufacturing and supply landscape is a much more
complex environment characterized by massive instability and volatility. Forecast error
continues to rise despite significant investments in time and money creating more sophis-
ticated algorithms for predicting the behavior of supply chains. There are three well-
known rules of forecasting that have not changed with this investment:
1. Forecasts are always in error.
2. The more detailed the forecast, the more error will be realized.
3. The further into the future the forecast goes, the more error will be realized.
There is a legacy of make to stock manufacturing strategies that are centered on
MRP and how it has been implemented traditionally. When considering today’s condi-
tions of shorter customer tolerance times with longer and more complicated supply net-
works, the need for holding stock at some level is a given for most manufacturers. The