Page 173 - Partition & Adsorption of Organic Contaminants in Environmental Systems
P. 173
164 CONTAMINANT SORPTION TO SOILS AND NATURAL SOLIDS
Whole peat
Uptake by Sorbent, Q (mg/g) 300
Peat HA
Humin
Muck HA
200
100
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6
Relative Concentration, C /S
e w
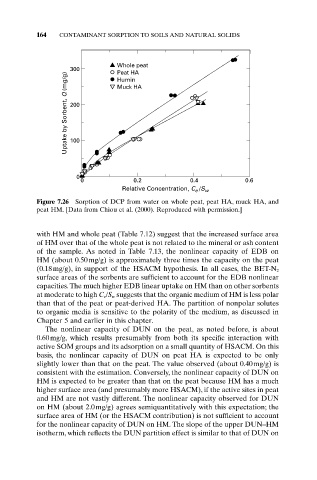
Figure 7.26 Sorption of DCP from water on whole peat, peat HA, muck HA, and
peat HM. [Data from Chiou et al. (2000). Reproduced with permission.]
with HM and whole peat (Table 7.12) suggest that the increased surface area
of HM over that of the whole peat is not related to the mineral or ash content
of the sample. As noted in Table 7.13, the nonlinear capacity of EDB on
HM (about 0.50mg/g) is approximately three times the capacity on the peat
(0.18mg/g), in support of the HSACM hypothesis. In all cases, the BET-N 2
surface areas of the sorbents are sufficient to account for the EDB nonlinear
capacities. The much higher EDB linear uptake on HM than on other sorbents
at moderate to high C e/S w suggests that the organic medium of HM is less polar
than that of the peat or peat-derived HA. The partition of nonpolar solutes
to organic media is sensitive to the polarity of the medium, as discussed in
Chapter 5 and earlier in this chapter.
The nonlinear capacity of DUN on the peat, as noted before, is about
0.60mg/g, which results presumably from both its specific interaction with
active SOM groups and its adsorption on a small quantity of HSACM. On this
basis, the nonlinear capacity of DUN on peat HA is expected to be only
slightly lower than that on the peat. The value observed (about 0.40mg/g) is
consistent with the estimation. Conversely, the nonlinear capacity of DUN on
HM is expected to be greater than that on the peat because HM has a much
higher surface area (and presumably more HSACM), if the active sites in peat
and HM are not vastly different. The nonlinear capacity observed for DUN
on HM (about 2.0mg/g) agrees semiquantitatively with this expectation; the
surface area of HM (or the HSACM contribution) is not sufficient to account
for the nonlinear capacity of DUN on HM. The slope of the upper DUN–HM
isotherm, which reflects the DUN partition effect is similar to that of DUN on