Page 191 - Partition & Adsorption of Organic Contaminants in Environmental Systems
P. 191
182 CONTAMINANT SORPTION TO SOILS AND NATURAL SOLIDS
1600
Apparent Solubility of p,p'-DDT (µg/L) 1200
800
400
0
0 1000 2000 3000 4000
Surfactant Concentration, X (mg/L)
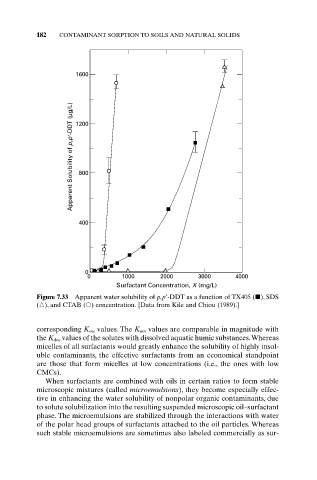
Figure 7.33 Apparent water solubility of p,p¢-DDT as a function of TX405 ( ), SDS
( ), and CTAB ( ) concentration. [Data from Kile and Chiou (1989).]
corresponding K mc values. The K mn values are comparable in magnitude with
the K doc values of the solutes with dissolved aquatic humic substances.Whereas
micelles of all surfactants would greatly enhance the solubility of highly insol-
uble contaminants, the effective surfactants from an economical standpoint
are those that form micelles at low concentrations (i.e., the ones with low
CMCs).
When surfactants are combined with oils in certain ratios to form stable
microscopic mixtures (called microemulsions), they become especially effec-
tive in enhancing the water solubility of nonpolar organic contaminants, due
to solute solubilization into the resulting suspended microscopic oil–surfactant
phase. The microemulsions are stabilized through the interactions with water
of the polar head groups of surfactants attached to the oil particles. Whereas
such stable microemulsions are sometimes also labeled commercially as sur-