Page 218 - Partition & Adsorption of Organic Contaminants in Environmental Systems
P. 218
SORPTION FROM VAPOR PHASE 209
40
Uptake by Peat, Q (mg/g) 30
20
10
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Relative Pressure, P/P°
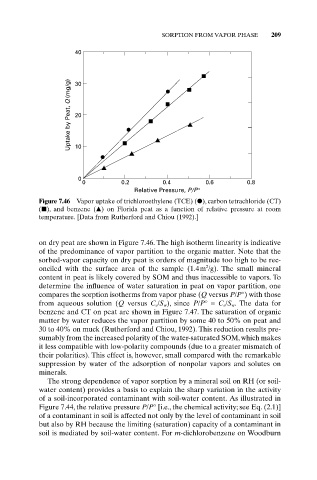
Figure 7.46 Vapor uptake of trichloroethylene (TCE) ( ), carbon tetrachloride (CT)
( ), and benzene ( ) on Florida peat as a function of relative pressure at room
temperature. [Data from Rutherford and Chiou (1992).]
on dry peat are shown in Figure 7.46. The high isotherm linearity is indicative
of the predominance of vapor partition to the organic matter. Note that the
sorbed-vapor capacity on dry peat is orders of magnitude too high to be rec-
2
onciled with the surface area of the sample (1.4m /g). The small mineral
content in peat is likely covered by SOM and thus inaccessible to vapors. To
determine the influence of water saturation in peat on vapor partition, one
compares the sorption isotherms from vapor phase (Q versus P/P°) with those
from aqueous solution (Q versus C e/S w), since P/P° = C e/S w. The data for
benzene and CT on peat are shown in Figure 7.47. The saturation of organic
matter by water reduces the vapor partition by some 40 to 50% on peat and
30 to 40% on muck (Rutherford and Chiou, 1992). This reduction results pre-
sumably from the increased polarity of the water-saturated SOM, which makes
it less compatible with low-polarity compounds (due to a greater mismatch of
their polarities). This effect is, however, small compared with the remarkable
suppression by water of the adsorption of nonpolar vapors and solutes on
minerals.
The strong dependence of vapor sorption by a mineral soil on RH (or soil-
water content) provides a basis to explain the sharp variation in the activity
of a soil-incorporated contaminant with soil-water content. As illustrated in
Figure 7.44, the relative pressure P/P° [i.e., the chemical activity; see Eq. (2.1)]
of a contaminant in soil is affected not only by the level of contaminant in soil
but also by RH because the limiting (saturation) capacity of a contaminant in
soil is mediated by soil-water content. For m-dichlorobenzene on Woodburn