Page 216 - Petroleum Geology
P. 216
193
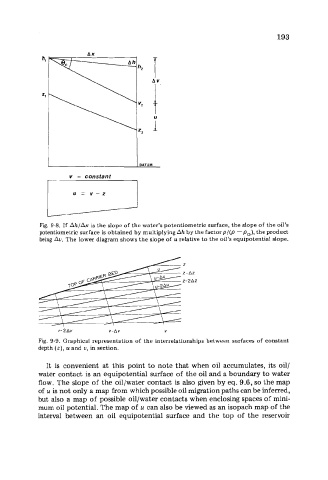
DATUM
7
I u = v-z I
Fig. 9-8. If Ah/Ax is the slope of the water’s potentiometric surface, the slope of the oil’s
potentiometric surface is obtained by multiplying Ah by the factor p/(p -Po), the product
being Au. The lower diagram shows the slope of u relative to the oil’s equipotential slope.
z
Z-AZ
2-2Az
v-2Av v-Av V
Fig. 9-9. Graphical representation of the interrelationships between surfaces of constant
depth (z), u and u, in section.
It is convenient at this point to note that when oil accumulates, its oil/
water contact is an equipotential surface of the oil and a boundary to water
flow. The slope of the oil/water contact is also given by eq. 9.6, so the map
of u is not only a map from which possible oil migration paths can be inferred,
but also a map of possible oil/water contacts when enclosing spaces of mini-
mum oil potential. The map of u can also be viewed as an isopach map of the
interval between an oil equipotential surface and the top of the reservoir