Page 149 - Phase Space Optics Fundamentals and Applications
P. 149
130 Chapter Four
1000 1000
W = 0 750 W = λ/2
40
40
α = 0°
Irradiance (a.u.) 500 500
α = 0°
750
250
0
0 250
15 15
W = 0 W = λ/2
40
40
α = 0.012°
α = 0.012°
Irradiance (a.u.) 10 5 10
5
0 0
8 8
W = 0 W = λ/2
40 6 40
α = 0.024°
α = 0.024°
Irradiance (a.u.) 4 4
6
2
0 2 0
–4.0 –2.0 0.0 2.0 4.0 –4.0 –2.0 0.0 2.0 4.0
Defocus coefficient: W (μm)
20
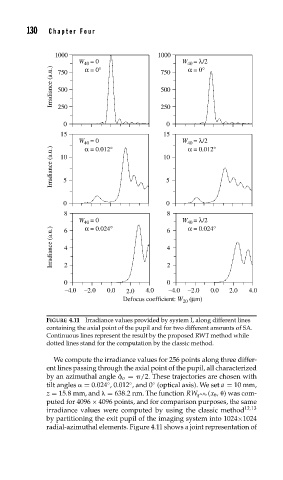
FIGURE 4.11 Irradiance values provided by system I, along different lines
containing the axial point of the pupil and for two different amounts of SA.
Continuous lines represent the result by the proposed RWT method while
dotted lines stand for the computation by the classic method.
We compute the irradiance values for 256 points along three differ-
ent lines passing through the axial point of the pupil, all characterized
by an azimuthal angle o = /2. These trajectories are chosen with
tilt angles = 0.024 ,0.012 , and 0 (optical axis). We set a = 10 mm,
◦
◦
◦
, o (x , ) was com-
z = 15.8 mm, and = 638.2 nm. The function RW q
puted for 4096 × 4096 points, and for comparison purposes, the same
irradiance values were computed by using the classic method 12,13
by partitioning the exit pupil of the imaging system into 1024×1024
radial-azimuthal elements. Figure 4.11 shows a joint representation of