Page 159 - Phase Space Optics Fundamentals and Applications
P. 159
140 Chapter Four
A normalized version of this axial irradiance is often used as a figure
of merit of the performance of the imaging system, namely, the SR
versus defocus, defined as
2
I (0,z) h
S(W 20 ) = ∝ RW t 0, arctan − (4.85)
I (0, 0) 2W 20
where h is the maximum lateral extent of the one-dimensional pupil
and W 20 stands for the one-dimensional version of the defocus coeffi-
cient defined in Eq. (4.51). Thus, the function S(W 20 ) can be analyzed in
a polar fashion in the two-dimensional domain of the WDF associated
with the pupil function t(x) or, equivalently, in terms of its associated
RWT.
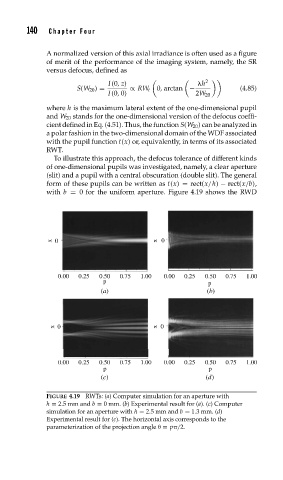
To illustrate this approach, the defocus tolerance of different kinds
of one-dimensional pupils was investigated, namely, a clear aperture
(slit) and a pupil with a central obscuration (double slit). The general
form of these pupils can be written as t(x) = rect(x/h) − rect(x/b),
with b = 0 for the uniform aperture. Figure 4.19 shows the RWD
x 0 x 0
0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00
p p
(a) (b)
x 0 x 0
0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00
p p
(c) (d)
FIGURE 4.19 RWTs: (a) Computer simulation for an aperture with
h = 2.5mmand b = 0 mm. (b) Experimental result for (a). (c) Computer
simulation for an aperture with h = 2.5mmand b = 1.3 mm. (d)
Experimental result for (c). The horizontal axis corresponds to the
parameterization of the projection angle = p /2.