Page 138 - Photoreactive Organic Thin Films
P. 138
4. PHOTOISOMERIZATION AND PHOTO-ORIENTATION OF AZO DYE IN FILMS OF POLYMER J \J
4.3 PHOTOISOM ERIZATION AND PHOTO-ORIENTATION OF AZOBENZEN ESI N
SUPRAMOLECULAR ASSEMBLIES: PHOTO-CONTROL OFTHE STRUCTURAL AND
OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF LANGMUIR-BLODGETT-KUHN MULTILAYERS OF HAIRY-
ROD AZO-POLYGLUTAM ATES
Hairy-rod molecules, consisting of rod-like molecules with covalently attached
53 56
flexible side chains " have been designed and used for forming nano-
structured systems by using the LBK deposition technique. The flexible side
chains enable the stiff molecules to be soluble in organic solvents and improve
their transfer through LBK deposition. At the air/water interface, the side
chains are oriented away from the water subphase, and the rods lay flat on
the interface. For small substrates (in comparison to the width of the trough),
the flow process during LBK deposition orients the rods parallel to the
dipping direction, and the side chains form a liquid-like matrix for the rods in
the reinforced liquid model. 54
Hairy-rod molecules containing azobenzene units in the side chains
57
can be assembled into LBK structures. The azobenzene molecules undergo
trans«-K:is photoisomerization under light irradiation of appropriate wavelength
and alter the structural properties of LBK films. We will discuss the photoinduced
movement of the azobenzene molecule in a series of LBK structures of azo-
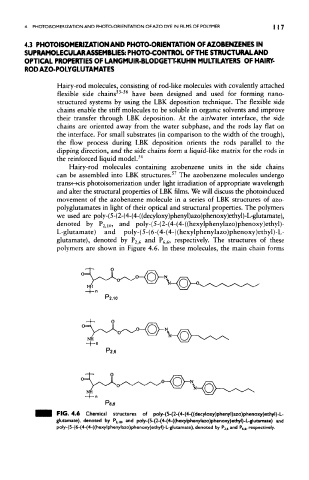
polyglutamates in light of their optical and structural properties. The polymers
we used are poly-(5-(2-(4-(4-((decyloxy)phenyl)azo)phenoxy)ethyl)-L-glutamate),
denoted by P 2,Kb and poly-(5-(2-(4-(4-((hexylphenylazo)phenoxy)ethyl)-
L-glutamate) and poly-(5-(6-(4-(4-((hexylphenylazo)phenoxy)ethyl)-L-
glutamate), denoted by P 2j<$ and P 6i6, respectively. The structures of these
polymers are shown in Figure 4.6. In these molecules, the main chain forms
P2.10
•—•{-- n
PIG. 4.6 Chemical structures of poly-(5-(2-(4-(4-((decyloxy)phenyl)azo)phenoxy)ethyl}-L-
ar
glutamate), denoted by P 2iio> »d poly-(5-(2-(4-(4-((hexylphenylazo)phenoxy)ethyl)-L-glutamate) and
poly-(5-(6-(4-(4-((hexylphenylazo)phenoxy)ethyl)-L-glutamate), denoted by P 2 , 4 and P 6 6, respectively.