Page 347 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 347
14/324 Absolute Risk Estimates
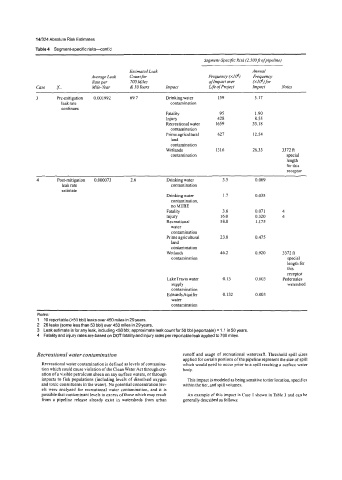
Table 4 Segment-specific risks-cont'd
Segment-Specific Risk (2SOOfi ofpipeline)
Estimated Leak Annual
Average Leak Countfor Frequency (XI@) Frequency
Rate per 700 Miles of Impact over (x106)f.r
Case $.. Mile-Year & SO Years Impact Life ofProject Impact Notes
3 Pre-mitigation 0.001992 69.1 Drinking water 159 3.17
leak rate contamination
continues
Fatality 95 1.90
Injury 428 8.55
Recreational water 1659 33.18
contamination
Prime agricultural 627 12.54
land
contamination
Wetlands 1316 26.33 3312 ft
contamination special
length
for this
receptor
4 Post-mitigation 0.000073 2.6 Drinking water 3.5 0.069
leak rate contamination
estimate
Drinking water 1.7 0.035
contamination,
no MTBE
Fatality 3.6 0.071 4
Injw 16.0 0.320 4
Recreational 58.8 1.175
water
contamination
Prime agricultural 23.8 0.475
land
contamination
Wetlands 46.2 0.920 3372 ft
contamination special
length for
this
receptor
Lake Travis water 0.13 0.003 Pedemales
supply watershed
contamination
Edwards Aquifer 0.132 0.003
water
contamination
Notes:
1 10 reportable (~50 bbl) leaks over450 miles in 29 years.
2 26 leaks (some less than 50 bbl) over450 miles in 29 years.
3 Leak estimate is for any leak, including 60 bbl; approximate leak count for 50 bbl (reportable) = 1.1 in 50 years.
4 Fatality and injury rates are based on DOTfatality and injury rates per reportable leak applied to 700 miles.
Recreational water contamination runoff and usage of recreational watercraft. Threshold spill sizes
applied for certain portions of the pipeline represent the size of spill
Recreational water contamination is defined as levels of contamina- which would need to occur prior to a spill reaching a surface water
tion which could cause violation ofthe Clean Water Act through cre- body.
ation of a visible pewoleurn sheen on any surface waters, or through
impacts to fish populations (including levels of dissolved oxygen This impact is modeled as being sensitive to tier location, specifics
and toxic constituents in the water). No potential concentration lev- within the tier, and spill volumes.
els were analyzed for recreational water contamination, and it is
possible that contaminant levels in excess of those which may result An example of this impact is Case I shown in Table 3 and can he
from a pipeline release already exist in watersheds from urban generally described as follows: