Page 192 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 192
Control Valves 179
Table 1
Maximum Flow Coefficients (C v)
Valve Ball Slot No. Plates C v C v
Size Dia. Length Each Slot w/Trim w/o Trim
1 4.25 7.40 8 45 53
1 1/2 5.50 9.58 16 98 120
2 6.50 11.32 16 195 220
3 8.00 13.93 18 410 480
4 9.75 16.58 20 765 860
6 13.25 23.08 25 1900 1990
Sizing valves for liquid flow
These equations for single-phase Newtonian liquid flow
assume that the liquid is non-viscous and neither cavitat-
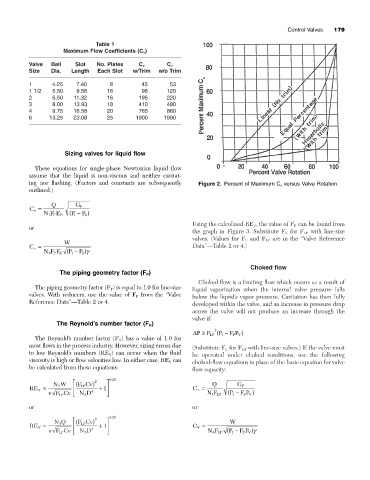
ing nor flashing. (Factors and constants are subsequently Figure 2. Percent of Maximum C v versus Valve Rotation.
outlined.)
Q G F
C v =
P - )
NF E R ( 1 P 2
P
1
Using the calculated RE V , the value of F R can be found from
or
the graph in Figure 3. Substitute F L for F LP with line-size
valves. (Values for F L and F LP are in the “Valve Reference
W
C v = Data”—Table 2 or 4.)
P - )g
6
PR
NF F ( 1 P 2
Choked flow
The piping geometry factor (F P )
Choked flow is a limiting flow which occurs as a result of
The piping geometry factor (F P ) is equal to 1.0 for line-size liquid vaporization when the internal valve pressure falls
valves. With reducers, use the value of F P from the “Valve below the liquid’s vapor pressure. Cavitation has then fully
Reference Data”—Table 2 or 4. developed within the valve, and an increase in pressure drop
across the valve will not produce an increase through the
valve if:
The Reynold’s number factor (F R )
2
DP ≥ F LP ( 1 F P V )
P -
F
The Reynold’s number factor (F R ) has a value of 1.0 for
most flows in the process industry. However, sizing errors due (Substitute F L for F LP with line-size valves.) If the valve must
to low Reynold’s numbers (RE V ) can occur when the fluid be operated under choked conditions, use the following
viscosity is high or flow velocities low. In either case, RE V can choked-flow equations in place of the basic equation for valve
be calculated from these equations: flow capacity:
.
NW ( È FCv) 2 ˘ 025 Q G F
3
LP
RE V = Í + ˙ 1 C v =
FCv Î ND 4 ˚ NF LP ( 1 F P )
P -
1
FV
2
LP
or or
.
NQ ( È FCv) 2 ˘ 025 W
4
LP
RE V = Í + ˙ 1 C V =
FCv Î ND 4 ˚ NF LP ( 1 F P V )g
P -
F
6
2
LP