Page 325 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 325
298 Chapter 16
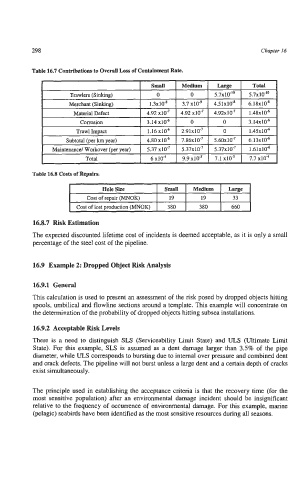
SmSU Medium Large Total
Trawlers (Sinking) 0 0 5.7x10-" 5.7~10-'~
Merchant (Sinhng) 1.3x1U8 3.7 xlU9 4.51~10-~ 6.18~10.~
Material Defect 4.92 xlU7 4.92 x107 4.92~10.~ 1.48~10-~
Corrosion 3.14 xl0" 0 0 3.14~10~
Trawl Impact 1.16 xl0" 2.91~10~ 0 1.45~10~
Subtotal (per km year) 4.80 x104 7.86~10~ 5.60~10-~ 6.13~10~
Maintenance/ Workover (Der year) 5.37 xlV7 5.37~10-~ 5.37~10.~ 1.61~10"
I Total I 6x104 I 9.9~10' I 7.1 xlO-' I 7.7 x104 I
Table 16.8 Costs of Repairs.
I Hole Size I Small I Medium I Large 1
Cost of repair (MNOK) 19 19 33
Cost of lost production (MNOK) 380 380 660
16.9 Example 2: Dropped Object Risk Analysis
16.9.1 General
This calculation is used to present an assessment of the risk posed by dropped objects hitting
spools, umbilical and flowline sections around a template. This example will concentrate on
the determination of the probability of dropped objects hitting subsea installations.
16.9.2 Acceptable Risk Levels
There is a need to distinguish SLS (Serviceability Limit State) and ULS (Ultimate Limit
State). For this example, SLS is assumed as a dent damage larger than 3.5% of the pipe
diameter, while TJLS corresponds to bursting due to internal over pressure and combined dent
and crack defects. The pipeline will not burst unless a large dent and a certain depth of cracks
exist simultaneously.
The principle used in establishing the acceptance criteria is that the recovery time (for the
most sensitive population) after an environmental damage incident should be insignificant
relative to the frequency of Occurrence of environmental damage. For this example, marine
(pelagic) seabirds have been identified as the most sensitive resources during all seasons.