Page 516 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 516
LCC Modeling as a Decision Making Tool in Pipeline Design 483
consequence costs, four separate costs, can be considered unplanned maintenance,
environmental damage and clean-up, loss of production and loss of human life.
In order to calculate these costs accurately, it is necessary to cany out a thorough analysis of
the possible consequences of pipeline failure. This can be simplified to the extreme
boundaries of these consequences. As in our case the following consequences can be
envisaged:
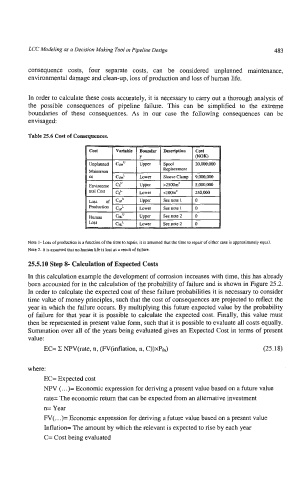
Table 25.6 Cost of Consequences.
Upper Seenote2 0
Note 1- Loss of production is a function of Ihe time to repair; it is assumed that the time to repair of either case is approximately equal
Note 2- it is assumed that no human life is lost as a result of failure.
25.5.10 Step 8- Calculation of Expected Costs
In this calculation example the development of corrosion increases with time, this has already
been accounted for in the calculation of the probability of failure and is shown in Figure 25.2.
In order to calculate the expected cost of these failure probabilities it is necessary to consider
time value of money principles, such that the cost of consequences are projected to reflect the
year in which the failure occurs. By multiplying this future expected value by the probability
of failure for that year it is possible to calculate the expected cost. Finally, this value must
then be represented in present value form, such that it is possible to evaluate all costs equally.
Summation over all of the years being evaluated gives an Expected Cost in terms of present
value:
EC= Z NPV(rate, n, (FV(inflation, n, C))xP,) (25.18)
where:
EC= Expected cost
NFV (. . .)= Economic expression for deriving a present value based on a future value
rate= The economic return that can be expected from an alternative investment
n= Year
FV(. . .)= Economic expression for deriving a future value based on a present value
Inflation= The amount by which the relevant is expected to rise by each year
C= Cost being evaluated