Page 254 - Plant design and economics for chemical engineers
P. 254
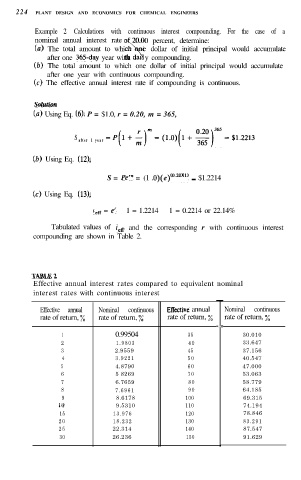
224 PLANT DESIGN AND ECONOMICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
Example 2 Calculations with continuous interest compounding. For the case of a
nominal annual interest rate 20.00 percent, determine:
(a> The total amount to which e dollar of initial principal would accumulate
\
after one 365day year with da1 y compounding.
(b) The total amount to which one dollar of initial principal would accumulate
after one year with continuous compounding.
(cl The effective annual interest rate if compounding is continuous.
s01uti0tl
(a) Using Eq. (6). P = $1.0, r = 0.20, m = 365,
S after 1 y e a r =P(1+$)~=(l.O)(1+~)16i=$12213
(b) Using Eq. (12),
S = PC? = (1 .O)(C)(~.~~~) = $1.2214
(cl Using Eq. (131,
leff = e’ - 1 = 1.2214 - 1 = 0.2214 or 22.14%
Tabulated values of i,, and the corresponding r with continuous interest
compounding are shown in Table 2.
Effective annual interest rates compared to equivalent nominal
interest rates with continuous interest
-
Effective annual Nominal continuous Efkctive annual Nominal continuous
rate of return, oA rate of return, oA rate of return, ‘A rate of return, %
_-
1 0.99504 35 30.010
2 1.9803 40 33.647
3 2.9559 45 37.156
4 3.9221 50 40.547
5 4.8790 60 47.000
6 5 8269 70 53.063
7 6.7659 80 58.779
8 7.6961 90 64.185
9 8.6178 100 69.315
10 9.5310 110 74.194
15 13.976 120 78.846
20 18.232 130 83.291
25 22.314 140 87.547
30 26.236 150 91.629