Page 251 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 251
Polyaniline-based nanocomposites for hydrogen storage 223
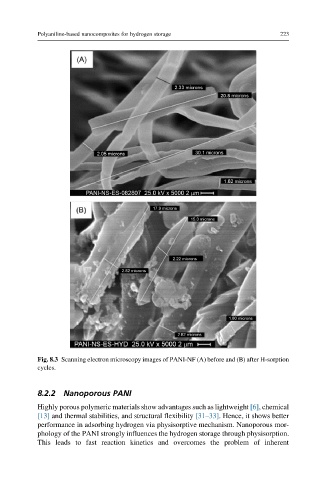
Fig. 8.3 Scanning electron microscopy images of PANI-NF (A) before and (B) after H-sorption
cycles.
8.2.2 Nanoporous PANI
Highly porous polymeric materials show advantages such as lightweight [6], chemical
[13] and thermal stabilities, and structural flexibility [31–33]. Hence, it shows better
performance in adsorbing hydrogen via physisorptive mechanism. Nanoporous mor-
phology of the PANI strongly influences the hydrogen storage through physisorption.
This leads to fast reaction kinetics and overcomes the problem of inherent