Page 332 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 332
300 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
100
700
600 Charge 99
Capacity (mAh g −1 ) 500 CNS-850 98 Coulombic efficiency (%)
Discharge
400
300
200 C 97
2C
96
5C
100
0 95
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
(A) Cycle number
Charge 100.5
600 Discharge
100.0
Capacity (mAh g −1 ) 400 CNS-850 99.5 Coulombic efficiency (%)
99.0
200
98.5
0 98.0
0 200 400 600 800 1000
(B) Cycle number
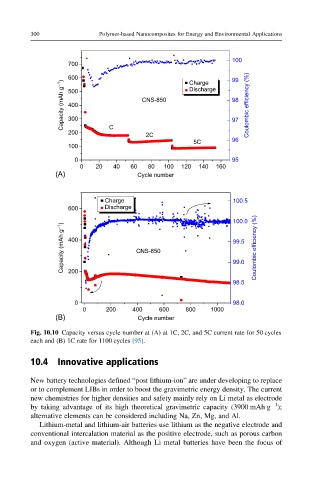
Fig. 10.10 Capacity versus cycle number at (A) at 1C, 2C, and 5C current rate for 50 cycles
each and (B) 1C rate for 1100 cycles [95].
10.4 Innovative applications
New battery technologies defined “post lithium-ion” are under developing to replace
or to complement LIBs in order to boost the gravimetric energy density. The current
new chemistries for higher densities and safety mainly rely on Li metal as electrode
1
by taking advantage of its high theoretical gravimetric capacity (3900 mAh g );
alternative elements can be considered including Na, Zn, Mg, and Al.
Lithium-metal and lithium-air batteries use lithium as the negative electrode and
conventional intercalation material as the positive electrode, such as porous carbon
and oxygen (active material). Although Li metal batteries have been the focus of