Page 443 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 443
400 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
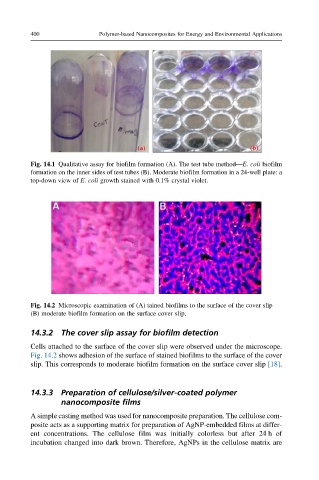
Fig. 14.1 Qualitative assay for biofilm formation (A). The test tube method—E. coli biofilm
formation on the inner sides of test tubes (B). Moderate biofilm formation in a 24-well plate: a
top-down view of E. coli growth stained with 0.1% crystal violet.
Fig. 14.2 Microscopic examination of (A) tained biofilms to the surface of the cover slip
(B) moderate biofilm formation on the surface cover slip.
14.3.2 The cover slip assay for biofilm detection
Cells attached to the surface of the cover slip were observed under the microscope.
Fig. 14.2 shows adhesion of the surface of stained biofilms to the surface of the cover
slip. This corresponds to moderate biofilm formation on the surface cover slip [18].
14.3.3 Preparation of cellulose/silver-coated polymer
nanocomposite films
A simple casting method was used for nanocomposite preparation. The cellulose com-
posite acts as a supporting matrix for preparation of AgNP-embedded films at differ-
ent concentrations. The cellulose film was initially colorless but after 24 h of
incubation changed into dark brown. Therefore, AgNPs in the cellulose matrix are