Page 139 - Power Electronics Handbook
P. 139
132 Power semiconductor protection
For clearance times which last over one cycle the fault current curves
must be kept below the rating of the power semiconductor, and even if the
fuse operates within one cycle the peak let-through current must be below
the ratin of the semiconductor. Fuses should also be designed with a low
9
ratio of i I to r.m.s. current rating. The r.m.s. current can be increased by
cooling the fuse in an air stream, or by mounting it on a busbar or a
heatsink, the i2t characteristic not being affected by this. Fuses must also
have a sufficient voltage-clearing capability, otherwise a high-voltage
source can cause a continuous arc under fault conditions, with loss of
protection. The arcing voltage should also be as low as possible to limit the
peak voltage which occurs across the circuit elements, but this is at the
expense of the i2t characteristic.
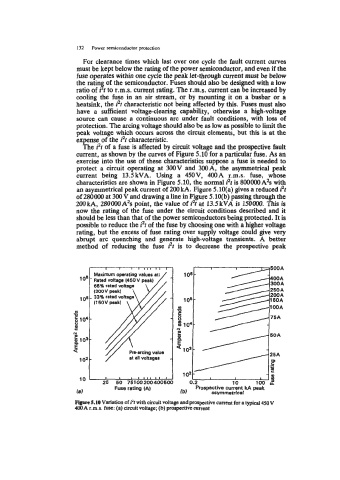
The i2t of a fuse is affected by circuit voltage and the prospective fault
current, as shown by the curves of Figure 5.10 for a particular fuse. As an
exercise into the use of these characteristics suppose a fuse is needed to
protect a circuit operating at 300V and WA, the asymmetrical peak
current being 13.5kVA. Using a 450V, 400A r.m.s. fuse, whose
characteristics are shown in Figure 5.10, the normal i2t is 800000A’s with
an asymmetrical peak current of 200kA. Figure 5.10(a) gives a reduced i2t
of 280000 at 300 V and drawing a line in Figure 5.10(b) passing through the
200kA, 280000A2s point, the value of i2t at 13.5kVA is 150000. This is
now the rating of the fuse under the circuit conditions described and it
should be less than that of the power semiconductors being protected. It is
possible to reduce the i2t of the fuse by choosing one with a higher voltage
rating, but the excess of fuse rating over supply voltage could give very
abrupt arc quenching and generate high-voltage transients. A better
method of reducing the fuse i2t is to decrease the prospective peak
1 1 I I I,, ,I I
Maximum Operating values at:
0‘ - Rated voltage (450 V peak)
06% rated voltage
(300V peak)
(150V peak)
u)
U
8 104-
a
102 -
Fuse rating (A)
(8)
FIpm 5.10 Variation of i2t with circuit voltage and prospective current for a typical 450V
400A r.m.s. fuse: (a) circuit voltage; (b) pmpective current