Page 195 - Power Electronics Handbook
P. 195
186 Phase-controlled rectification and inversion
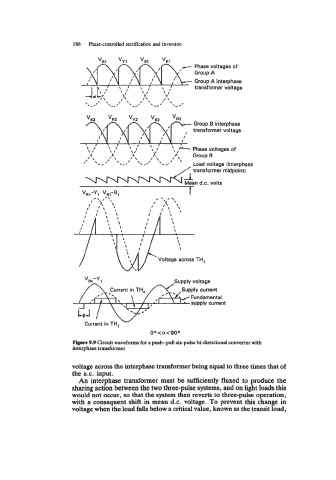
Phase voltages of
Group A
Group A interphase
transformer voltage
Group B interphase
transformer voltage
1 I \ 1 \ \,- Phase voltages of
\I \I \I ): Group B
,IK\, ,A ,fi\
,I<,, ,I' , \
' .#' './ '. -* Load voltage (interphase
.-a
transformer midpoint)
Mean d.c. volts
f
vRl-yl VRl-Bl
Voltage across TH,
00 < a<900
Figure 9.9 Circuit waveforms for a push-pull six-pulse bi-directional converter with
interphase transformer
voltage across the interphase transformer being equal to three times that of
the a.c. input.
An interphase transformer must be sufficiently fluxed to produce the
sharing action between the two three-pulse systems, and on light loads this
would not occur, so that the system then reverts to three-pulse operation,
with a consequent shift in mean d.c. voltage. To prevent this change in
voltage when the load falls below a critical value, known as the transit load,