Page 61 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 61
44 Chapter Four
TABLE 4.1 Some Effects of Harmonics
At Effect
Circuit breakers Malfunction
Capacitor banks Overheating
Insulation breakdown
Failure of internal fuses
Protection equipment False tripping
No tripping
Measuring devices Wrong measurements
Transformers, reactors Overheating
Motors Increased noise level
Overheating
Additional vibrations
Telephones Noise with the respective harmonic
frequency
Lines Overheating
Electronic devices Wrong pulses on data transmission
Over-/undervoltage
Flickering screens
Incandescent lamps Reduced lifetime
Flicker
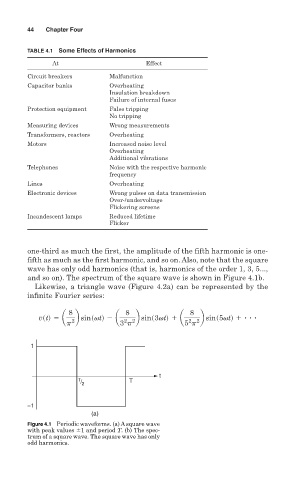
one-third as much the first, the amplitude of the fifth harmonic is one-
fifth as much as the first harmonic, and so on. Also, note that the square
wave has only odd harmonics (that is, harmonics of the order 1, 3, 5...,
and so on). The spectrum of the square wave is shown in Figure 4.1b.
Likewise, a triangle wave (Figure 4.2a) can be represented by the
infinite Fourier series:
8 8 8
vstd 5 a 2 b sinsvtd 2 a 2 2 b sins3vtd 1 a 2 2 b sins5vtd 1 ???
p 3 p 5 p
1
t
T / 2 T
−1
(a)
Figure 4.1 Periodic waveforms. (a) A square wave
with peak values 1 and period T. (b) The spec-
trum of a square wave. The square wave has only
odd harmonics.