Page 58 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 58
Voltage Distortion 41
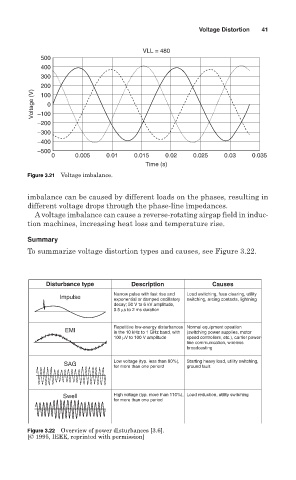
VLL = 480
500
400
300
200
Voltage (V) −100 0
100
−200
−300
−400
−500
0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 0.03 0.035
Time (s)
Figure 3.21 Voltage imbalance.
imbalance can be caused by different loads on the phases, resulting in
different voltage drops through the phase-line impedances.
A voltage imbalance can cause a reverse-rotating airgap field in induc-
tion machines, increasing heat loss and temperature rise.
Summary
To summarize voltage distortion types and causes, see Figure 3.22.
Disturbance type Description Causes
Narrow pulse with fast rise and Load switching, fuse clearing, utility
Impulse exponential or damped oscillatory switching, arcing contacts, lightning
decay; 50 V to 6 kV amplitude,
0.5 µs to 2 ms duration
Repetitive low-energy disturbances Normal equipment opeation
EMI in the 10 kHz to 1 GHz band, with (switching power supplies, motor
100 µV to 100 V amplitude speed controllers, etc.), carrier power-
line communication, wireless
broadcasting
Low voltage (typ. less than 80%), Starting heavy load, utility switching,
SAG for more than one periord ground fault
Swell High voltage (typ. more than 110%), Load reduction, utility switching
for more than one period
Figure 3.22 Overview of power disturbances [3.6].
[© 1995, IEEE, reprinted with permission]