Page 73 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 73
56 Chapter Four
i b
i c
i a
c
a
R R R
i n
b
(a)
i c
i a
−120°
i b
(b)
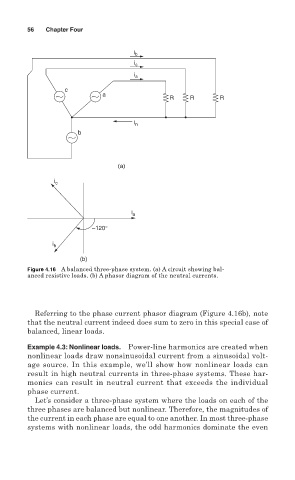
Figure 4.16 A balanced three-phase system. (a) A circuit showing bal-
anced resistive loads. (b) A phasor diagram of the neutral currents.
Referring to the phase current phasor diagram (Figure 4.16b), note
that the neutral current indeed does sum to zero in this special case of
balanced, linear loads.
Example 4.3: Nonlinear loads. Power-line harmonics are created when
nonlinear loads draw nonsinusoidal current from a sinusoidal volt-
age source. In this example, we’ll show how nonlinear loads can
result in high neutral currents in three-phase systems. These har-
monics can result in neutral current that exceeds the individual
phase current.
Let’s consider a three-phase system where the loads on each of the
three phases are balanced but nonlinear. Therefore, the magnitudes of
the current in each phase are equal to one another. In most three-phase
systems with nonlinear loads, the odd harmonics dominate the even