Page 86 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 86
Harmonic Current Sources 69
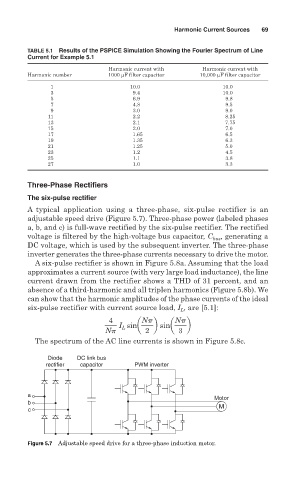
TABLE 5.1 Results of the PSPICE Simulation Showing the Fourier Spectrum of Line
Current for Example 5.1
Harmonic current with Harmonic current with
Harmonic number 1000 µF filter capacitor 10,000 µF filter capacitor
1 10.0 10.0
3 9.4 10.0
5 6.9 9.8
7 4.8 9.5
9 3.0 9.0
11 2.2 8.25
13 2.1 7.75
15 2.0 7.0
17 1.65 6.5
19 1.35 6.3
21 1.25 5.0
23 1.2 4.5
25 1.1 3.8
27 1.0 3.3
Three-Phase Rectifiers
The six-pulse rectifier
A typical application using a three-phase, six-pulse rectifier is an
adjustable speed drive (Figure 5.7). Three-phase power (labeled phases
a, b, and c) is full-wave rectified by the six-pulse rectifier. The rectified
voltage is filtered by the high-voltage bus capacitor, C bus , generating a
DC voltage, which is used by the subsequent inverter. The three-phase
inverter generates the three-phase currents necessary to drive the motor.
A six-pulse rectifier is shown in Figure 5.8a. Assuming that the load
approximates a current source (with very large load inductance), the line
current drawn from the rectifier shows a THD of 31 percent, and an
absence of a third-harmonic and all triplen harmonics (Figure 5.8b). We
can show that the harmonic amplitudes of the phase currents of the ideal
six-pulse rectifier with current source load, I , are [5.1]:
L
4 Np Np
I sina b sina b
L
Np 2 3
The spectrum of the AC line currents is shown in Figure 5.8c.
Diode DC link bus
rectifier capacitor PWM inverter
a Motor
b
c M
Figure 5.7 Adjustable speed drive for a three-phase induction motor.