Page 34 - Practical Control Engineering a Guide for Engineers, Managers, and Practitioners
P. 34
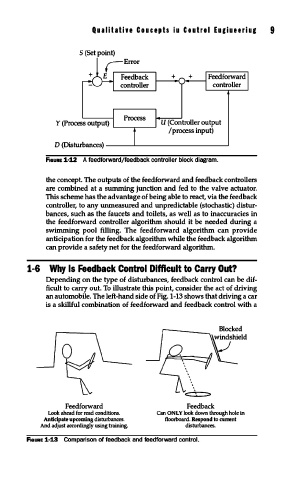
Qualitative Couceph iu Coutrol Eugiueeriug 9
Feedforward
controller
U (Controller output
/process input)
D (Disturbances) ---...L...-------------1
FIGURE 1·12 A feedforward/feedback controller block diagram.
the concept. The outputs of the feedforward and feedback controllers
are combined at a summing junction and fed to the valve actuator.
This scheme has the advantage of being able to react, via the feedback
controller, to any unmeasured and unpredictable (stochastic) distur-
bances, such as the faucets and toilets, as well as to inaccuracies in
the feedforward controller algorithm should it be needed during a
swimming pool filling. The feedforward algorithm can provide
anticipation for the feedback algorithm while the feedback algorithm
can provide a safety net for the feedforward algorithm.
1-6 Why Is Feedback Control Difficult to Carry Out?
Depending on the type of disturbances, feedback control can be dif-
ficult to carry out. To illustrate this point, consider the act of driving
an automobile. The left-hand side of Fig. 1-13 shows that driving a car
is a skillful combination of feedforward and feedback control with a
Feedforward Feedback
Look ahead for read conditions. Can ONLY look down through hole in
Anticipate upcoming disturbances. floorboard. Respond to current
And adjust accordingly using training. disturbances.
FIGURE 1·13 Comparison of feedback and feedforward control.