Page 82 - Practical Power System and Protective Relays Commissioning
P. 82
Transmission Lines Theory Testing and Commissioning Chapter | 6 79
In this mode of transmission a three-phase 50 or 60 Hz voltage and cur-
rents are converted to DC voltage. Currents transmitted on a bipolar line con-
sist of two conductors at the end of the line converted back to AC voltages
and currents by inverters.
The advantage of this system is that it can connect between two different
frequency AC systems. It can also be used in long underground cables or
underwater submarine cables, and is very good for long distance overhead
transmission. It is used for transmission lines over 640 km and over 32 km
for underground cables.
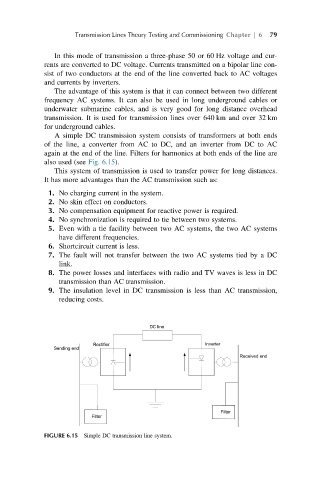
A simple DC transmission system consists of transformers at both ends
of the line, a converter from AC to DC, and an inverter from DC to AC
again at the end of the line. Filters for harmonics at both ends of the line are
also used (see Fig. 6.15).
This system of transmission is used to transfer power for long distances.
It has more advantages than the AC transmission such as:
1. No charging current in the system.
2. No skin effect on conductors.
3. No compensation equipment for reactive power is required.
4. No synchronization is required to tie between two systems.
5. Even with a tie facility between two AC systems, the two AC systems
have different frequencies.
6. Shortcircuit current is less.
7. The fault will not transfer between the two AC systems tied by a DC
link.
8. The power losses and interfaces with radio and TV waves is less in DC
transmission than AC transmission.
9. The insulation level in DC transmission is less than AC transmission,
reducing costs.
FIGURE 6.15 Simple DC transmission line system.