Page 231 - Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation 2E
P. 231
216 Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation
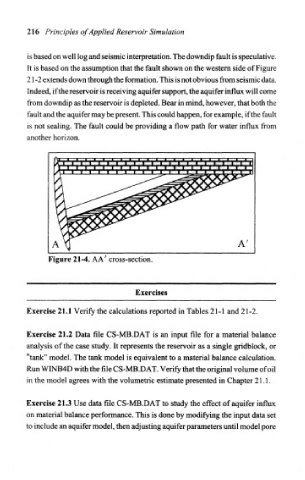
is based on well log and seismic interpretation. The downdip fault is speculative.
It is based on the assumption that the fault shown on the western side of Figure
21-2 extends down through the formation. This is not obvious from seismic data.
Indeed, if the reservoir is receiving aquifer support, the aquifer influx will come
from downdip as the reservoir is depleted. Bear in mind, however, that both the
fault and the aquifer may be present. This could happen, for example, if the fault
is not sealing. The fault could be providing a flow path for water influx from
another horizon.
Figure 21-4. AA' cross-section.
Exercises
Exercise 21.1 Verify the calculations reported in Tables 21-1 and 21-2.
Exercise 21.2 Data file CS-MB.DAT is an input file for a material balance
analysis of the case study. It represents the reservoir as a single gridblock, or
"tank" model. The tank model is equivalent to a material balance calculation.
Run WINB4D with the file CS-MB.DAT. Verify that the original volume of oil
in the model agrees with the volumetric estimate presented in Chapter 21.1.
Exercise 21.3 Use data file CS-MB.DAT to study the effect of aquifer influx
on material balance performance. This is done by modifying the input data set
to include an aquifer model, then adjusting aquifer parameters until model pore