Page 142 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 142
130 CHAPTER 6
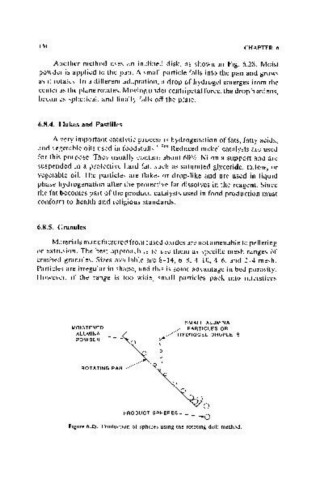
Another method uses an inclined disk, as shown in Fig. 6.28. Moist
powder is applied to the pan. A small particle falls into the pan and grows
as it rotates. In a different adaptation, a drop of hydrogel emerges from the
center as the plane rotates. Moving under centripetal force, the drop hardens,
becomes spherical, and finally falls off the plate.
6.S.4. Flakes and Pastilles
A very important catalytic process is hydrogenation of fats, fatty acids,
and vegetable oils used in foodstuffs. (190) Reduced nickel catalysts are used
for this purpose. They usually contain about 60% Ni on a support and are
suspended in a protective hard fat, such as saturated glyceride, tallow, or
vegetable oil. The particles are flake- or drop-like and are used in liquid
phase hydrogenation after the protective fat dissolves in the reagent. Since
the fat becomes part of the product, catalysts used in food production must
conform to health and religious standards.
6.S.S. Granules
Materials manufactured from fused oxides are not amenable to pelleting
or extrusion. The best approach is to use them as specific mesh ranges of
crushed granules. Sizes available are 8-14, 6-8, 4-10, 4-6, and 2-4 mesh.
Particles are irregular in shape, and this is some advantage in bed porosity.
However, if the range is too wide, small particles pack into interstices
~ SMALL ALUMINA
MOISTENED PARTICLES OR
ALUMINA o/HVDROGEL DROPLETS
POWDER
o
o
o
o
ROTATING PAN
o
PRODUCT SPHERES --...0
Figure 6.28. Production of spheres using the rotating dish method.