Page 88 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 88
CATALYTIC MATERIALS 7S
TABLE 4.10. Reactions
Catalyzed by Solid Acids
Cracking of C-C bonds
Alkyl group isomerization
Double bond isomerization
Dealkylation
Dehydroxylation
Dehydrogenation
Polymerization
Oligomization
Cyclization
Alkylation
"Coke" formation
excluded. Also called "molecular sieves," zeolites possess the ability to be
shape and size selective in catalytic molecular rearrangements. (133)
Second, ions within the cavities are easily exchanged with a large
number of altervalent ions. These ions exert large electrostatic or polarizing
forces across the small dimensions of the cavity. Electron distribution shifts
in acidic hydroxyl groups may be tailored to give acidities 10 times larger
4
than in SiO r AI 20 3 • They are indeed "super acids.,,(134)
(')
I
0
)(
>-
I-
> 2
i=
()
oc(
z
0
l-
e:(
....J
>-
:x::
....J
oc(
W
Cl
W
Z
w
:2
;:)
() 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
ACID AMOUNT, m mole g-1
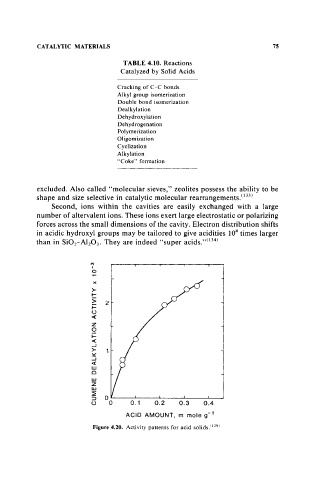
Figure 4.20. Activity patterns for acid solids. 1t291