Page 86 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 86
CATALYTIC MATERIALS 73
-
I
0) 0.4
<I)
0
E
E 0.3
..:
z
::>
0 0.2
~
c(
0
U 0.1
c(
0
+4 -5
ACIDITY, p Ka
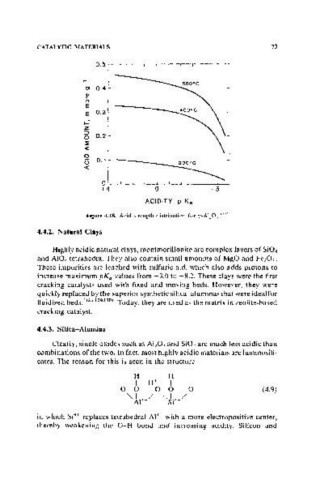
Figure 4.18. Acid strength distribution for y-AI20, .'SS)
4.4.2. Natural Clays
Highly acidic natural clays, montmorillonite are complex layers of Si0 4
and Al0 4 tetrahedra. They also contain small amounts of MgO and Fe 20 3 •
These impurities are leached with sulfuric aid, which also adds protons to
increase maximum pKa values from -3.0 to -8.2. These clays were the first
cracking catalysts used with fixed and moving beds. However, they were
quickly replaced by the superior synthetic silica-aluminas that were ideal for
fluidized beds. (128.129,130) Today, they are used as the matrix in zeolite-based
cracking catalyst.
4.4.3. Silica-Alumina
Clearly, single oxides such as Al 20 3 and Si0 2 are much less acidic than
combinations of the two. In fact, most highly acidic materials are luminosili-
cates. The reason for this is seen in the structure
H H
1 H+ 1
o 0 0 0 0 (4.9)
".1 / ".1 /
AlH Si 4 +
in which Si + replaces tetrahedral A1 + with a more electropositive center,
3
4
thereby weakening the O-H bond and increasing acidity. Silicon and