Page 234 - Process Modelling and Simulation With Finite Element Methods
P. 234
Geometric Continuation 22 1
You caught that, right? The Stationary Nonlinear solver. Why? Because
not only is this the default for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations, the
linear solver is not an option. It actually takes two iterations for FEMLAB to be
convinced it has converged, although the initial error being lo-'* might have
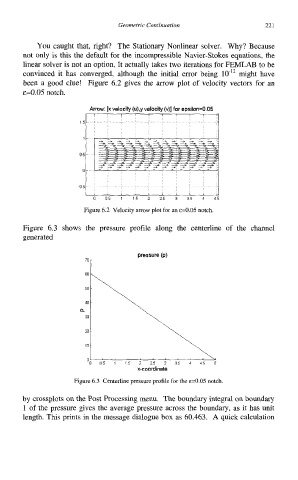
been a good clue! Figure 6.2 gives the arrow plot of velocity vectors for an
~=0.05 notch.
Arrow: [x velocity (u),y velocity (v)] for epsilon=O 05
1 5 1
Figure 6.2 Velocity arrow plot for an &=0.05 notch.
Figure 6.3 shows the pressure profile along the centerline of the channel
generated
70 -
60
50 -
20
10
Figure 6.3 Centerline pressure profile for the &=0.05 notch.
by crossplots on the Post Processing menu. The boundary integral on boundary
1 of the pressure gives the average pressure across the boundary, as it has unit
length. This prints in the message dialogue box as 60.463. A quick calculation