Page 52 - Process Modelling and Simulation With Finite Element Methods
P. 52
FEMLAB and the Basics of Numerical Analysis 39
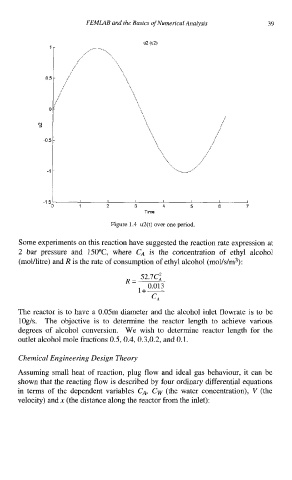
-1 4
I
1 I 2 I 3 I 4 I 5 6 I 7 I
Time
Figure 1.4 u2(t) over one period.
Some experiments on this reaction have suggested the reaction rate expression at
2 bar pressure and 15OoC, where C, is the concentration of ethyl alcohol
(mol/litre) and R is the rate of consumption of ethyl alcohol (moVs/m3):
R=- 52.7Ci
l+- 0.013
c.4
The reactor is to have a 0.05m diameter and the alcohol inlet flowrate is to be
lOg/s. The objective is to determine the reactor length to achieve various
degrees of alcohol conversion. We wish to determine reactor length for the
outlet alcohol mole fractions 0.5,0.4, 0.3,0.2, and 0.1.
Chemical Engineering Design Theory
Assuming small heat of reaction, plug flow and ideal gas behaviour, it can be
shown that the reacting flow is described by four ordinary differential equations
in terms of the dependent variables C,, CW (the water concentration), V (the
velocity) and x (the distance along the reactor from the inlet):