Page 113 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 113
CFA, distributed emission [continuous-cathode] CROWBAR 103
mode of operation is typical to linear-format CFAs, although
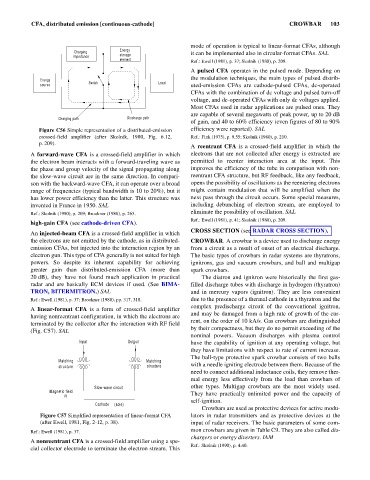
Energy
Charging it can be implemented also in circular-format CFAs. SAL
impedance storage
element
Ref.: Ewell (1981), p. 37; Skolnik (1980), p. 209.
A pulsed CFA operates in the pulsed mode. Depending on
the modulation techniques, the main types of pulsed distrib-
Energy
source Switch Load uted-emission CFAs are cathode-pulsed CFAs, dc-operated
CFAs with the combination of dc voltage and pulsed turn-off
voltage, and dc-operated CFAs with only dc voltages applied.
Most CFAs used in radar applications are pulsed ones. They
are capable of several megawatts of peak power, up to 20 dB
Charging path Discharge path
of gain, and 40 to 60% efficiency (even figures of 80 to 90%
Figure C56 Simple representation of a distributed-emission efficiency were reported). SAL
crossed-field amplifier (after Skolnik, 1980, Fig. 6.12, Ref.: Fink (1975), p. 9.55; Skolnik (1980), p. 210.
p. 209).
A reentrant CFA is a crossed-field amplifier in which the
A forward-wave CFA is a crossed-field amplifier in which electrons that are not collected after energy is extracted are
the electron beam interacts with a forward-traveling wave as permitted to reenter interaction area at the input. This
the phase and group velocity of the signal propagating along improves the efficiency of the tube in comparison with non-
the slow-wave circuit are in the same direction. In compari- reentrant CFA structure, but RF feedback, like any feedback,
son with the backward-wave CFA, it can operate over a broad opens the possibility of oscillations as the reentering electrons
range of frequencies (typical bandwidth is 10 to 20%), but it might contain modulation that will be amplified when the
has lower power efficiency than the latter. This structure was next pass through the circuit occurs. Some special measures,
invented in France in 1950. SAL including debunching of electron stream, are employed to
Ref.: Skolnik (1980), p. 209; Brookner (1988), p. 263. eliminate the possibility of oscillation. SAL
Ref.: Ewell (1981), p. 41; Skolnik (1980), p. 209.
high-gain CFA (see cathode-driven CFA).
CROSS SECTION (see RADAR CROSS SECTION).
An injected-beam CFA is a crossed-field amplifier in which
the electrons are not emitted by the cathode, as in distributed- CROWBAR. A crowbar is a device used to discharge energy
emission CFAs, but injected into the interaction region by an from a circuit as a result of onset of an electrical discharge.
electron gun. This type of CFA generally is not suited for high The basic types of crowbars in radar systems are thyratrons,
powers. So despite its inherent capability for achieving ignitrons, gas and vacuum crowbars, and ball and multigap
greater gain than distributed-emission CFA (more than spark crowbars.
20 dB), they have not found much application in practical The diatron and ignitron were historically the first gas-
radar and are basically ECM devices if used. (See BIMA- filled discharge tubes with discharge in hydrogen (thyratron)
TRON, BITERMITRON.) SAL and in mercury vapors (ignitron). They are less convenient
Ref.: Ewell (1981), p. 37; Brookner (1988), pp. 317, 318. due to the presence of a thermal cathode in a thyratron and the
complex predischarge circuit of the conventional ignitron,
A linear-format CFA is a form of crossed-field amplifier
and may be damaged from a high rate of growth of the cur-
having nonreentrant configuration, in which the electrons are
rent, on the order of 10 kA/s. Gas crowbars are distinguished
terminated by the collector after the interaction with RF field
by their compactness, but they do no permit exceeding of the
(Fig. C57). SAL
nominal powers. Vacuum discharges with plasma control
Input Output have the capability of ignition at any operating voltage, but
they have limitations with respect to rate of current increase.
The ball-type protective spark crowbar consists of two balls
Matching Matching
structure structure with a needle igniting electrode between them. Because of the
need to connect additional inductance coils, they remove ther-
mal energy less effectively from the load than crowbars of
Slow-wave circuit other types. Multigap crowbars are the most widely used.
Magnetic field
They have practically unlimited power and the capacity of
self-ignition.
Cathode (sole)
Crowbars are used as protective devices for active modu-
Figure C57 Simplified representation of linear-format CFA lators in radar transmitters and as protective devices at the
(after Ewell, 1981, Fig. 2-12, p. 38). input of radar receivers. The basic parameters of some com-
Ref.: Ewell (1981), p. 37. mon crowbars are given in Table C9. They are also called dis-
chargers or energy diverters. IAM
A nonreentrant CFA is a crossed-field amplifier using a spe-
Ref.: Skolnik (1990), p. 4.40.
cial collector electrode to terminate the electron stream. This