Page 151 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 151
display, bright display, detection 141
In radar, the use of color displays makes it possible to
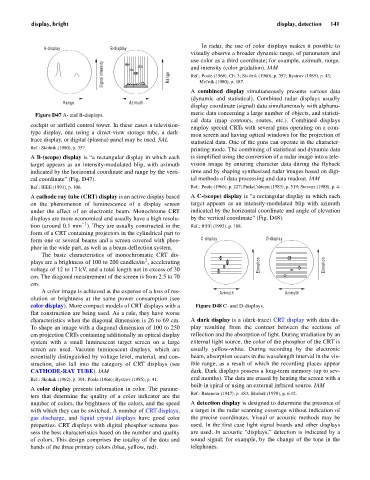
A-display B-display
visually observe a broader dynamic range, of parameters and
use color as a third coordinate; for example, azimuth, range,
Signal intensity Range and intensity (color gradation). IAM
Ref.: Poole (1966), Ch. 3; Skolnik (1980), p. 357; Bystrov (1985), p. 43;
Mel'nik (1980), p. 187.
A combined display simultaneously presents various data
(dynamic and statistical). Combined radar displays usually
Range Azimuth
display coordinate (signal) data simultaneously with alphanu-
meric data concerning a large number of objects, and statisti-
Figure D47 A- and B-displays.
cal data (map contours, routes, etc.). Combined displays
cockpit or airfield control tower. In these cases a television-
employ special CRTs with several guns operating on a com-
type display, one using a direct-view storage tube, a dark-
mon screen and having optical windows for the projection of
trace display, or digital (plasma) panel may be used. SAL
statistical data. One of the guns can operate in the character-
Ref.: Skolnik (1980), p. 357.
printing mode. The combining of statistical and dynamic data
A B-(scope) display is “a rectangular display in which each is simplified using the conversion of a radar image into a tele-
target appears as an intensity-modulated blip, with azimuth vision image by entering character data during the flyback
indicated by the horizontal coordinate and range by the verti- time and by shaping synthesized radar images based on digi-
cal coordinate” (Fig. D47). tal methods of data processing and data readout. IAM
Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 100. Ref.: Poole (1966), p. 227; Finkel’shteyn (1983), p. 519; Stevens (1988), p. 4.
A cathode ray tube (CRT) display is an active display based A C-(scope) display is “a rectangular display in which each
on the phenomenon of luminescence of a display screen target appears as an intensity-modulated blip with azimuth
under the effect of an electronic beam. Monochrome CRT indicated by the horizontal coordinate and angle of elevation
displays are more economical and usually have a high resolu- by the vertical coordinate” (Fig. D48).
- 1
tion (around 0.1 mm ). They are usually constructed in the Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 168.
form of a CRT containing projectors in the cylindrical part to
form one or several beams and a screen covered with phos- C-display D-display
phor in the wide part, as well as a beam-deflection system.
The basic characteristics of monochromatic CRT dis-
2
plays are a brightness of 100 to 200 candles/m , accelerating Elevation Elevation
voltage of 12 to 17 kV, and a total length not in excess of 30
cm. The diagonal measurement of the screen is from 2.5 to 70
cm.
A color image is achieved at the expense of a loss of res- Azimuth Azimuth
olution or brightness at the same power consumption (see
color display). More compact models of CRT displays with a Figure D48 C- and D-displays.
flat construction are being used. As a rule, they have worse
characteristics when the diagonal dimension is 26 to 69 cm. A dark display is a (dark-trace) CRT display with data dis-
To shape an image with a diagonal dimension of 100 to 250 play resulting from the contrast between the sections of
cm projection CRTs containing additionally an optical display reflection and the absorption of light. During irradiation by an
system with a small luminescent target screen on a large external light source, the color of the phosphor of the CRT is
screen are used. Vacuum luminescent displays, which are usually yellow-white. During recording by the electronic
essentially distinguished by voltage level, material, and con- beam, absorption occurs in the wavelength interval in the vis-
struction, also fall into the category of CRT displays (see ible range, as a result of which the recording places appear
CATHODE-RAY TUBE). IAM dark. Dark displays possess a long-term memory (up to sev-
Ref.: Skolnik (1962), p. 391; Poole (1966); Bystrov (1985), p. 41. eral months). The data are erased by heating the screen with a
built-in spiral or using an external infrared source. IAM
A color display presents information in color. The parame-
Ref.: Ridenour (1947), p. 483; Skolnik (1970), p. 6.12.
ters that determine the quality of a color indicator are the
number of colors, the brightness of the colors, and the speed A detection display is designed to determine the presence of
with which they can be switched. A number of CRT displays, a target in the radar scanning coverage without indication of
gas discharge, and liquid crystal displays have good color the precise coordinates. Visual or acoustic methods may be
properties. CRT displays with digital phosphor screens pos- used. In the first case light signal boards and other displays
sess the best characteristics based on the number and quality are used. In acoustic “displays,” detection is indicated by a
of colors. This design comprises the totality of the dots and sound signal; for example, by the change of the tone in the
bands of the three primary colors (blue, yellow, red). telephones.