Page 152 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 152
142 display, detection display, gas-discharge
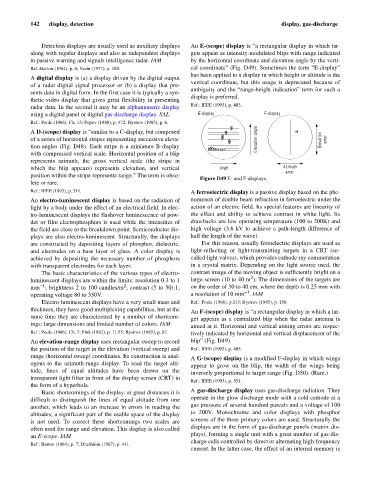
Detection displays are usually used as auxiliary displays An E-(scope) display is “a rectangular display in which tar-
along with regular displays and also as independent displays gets appear as intensity-modulated blips with range indicated
in passive warning and signals intelligence radar. IAM by the horizontal coordinate and elevation angle by the verti-
Ref.:Barton (1964), p. 6; Vasin (1977), p. 180. cal coordinate” (Fig. D49). Sometimes the term “E-display”
has been applied to a display in which height or altitude is the
A digital display is (a) a display driven by the digital output
vertical coordinate, but this usage is deprecated because of
of a radar digital signal processor or (b) a display that pre-
ambiguity and the “range-height indication” term for such a
sents data in digital form. In the first case it is typically a syn-
display is preferred.
thetic-video display that gives great flexibility in presenting
radar data. In the second it may be an alphanumeric display Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 403.
using a digital panel or digital gas-discharge display. SAL E-display F-display
Ref.: Poole (1966), Ch. 13; Popov (1980), p. 472; Bystrov (1985), p. 6.
A D-(scope) display is “similar to a C-display, but composed
of a series of horizontal stripes representing successive eleva- Elevation angle Elevation error
tion angles (Fig. D48). Each stripe is a miniature B-display
with compressed vertical scale. Horizontal position of a blip
represents azimuth, the gross vertical scale (the stripe in
which the blip appears) represents elevation, and vertical Range Azimuth
error
position within the stripe represents range.” The term is obso-
Figure D49 E- and F-displays.
lete or rare.
Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 311. A ferroelectric display is a passive display based on the phe-
An electro-luminescent display is based on the radiation of nomenon of double beam refraction in ferroelectric under the
light by a body under the effect of an electrical field. In elec- action of an electric field. Its special features are linearity of
tro-luminescent displays the flashover luminescence of pow- the effect and ability to achieve contrast in white light. Its
der or film electrophosphors is used while the intensities of drawbacks are low operating temperature (100 to 200K) and
the field are close to the breakdown point. Semiconductor dis- high voltage (3.6 kV to achieve a path-length difference of
plays are also electro-luminescent. Structurally, the displays half the length of the wave).
are constructed by depositing layers of phosphor, dielectric, For this reason, usually ferroelectric displays are used as
and electrodes on a base layer of glass. A color display is light-reflecting or light-transmitting targets in a CRT (so-
achieved by depositing the necessary number of phosphors called light valves), which provides cathode ray commutation
with transparent electrodes for each layer. in a crystal matrix. Depending on the light source used, the
The basic characteristics of the various types of electro- contrast image of the moving object is sufficiently bright on a
2
luminescent displays are within the limits: resolution 0.3 to 1 large screen (10 to 40 m ). The dimensions of the targets are
2
- 1
mm ; brightness 2 to 100 candles/m ; contrast (5 to 50):1; on the order of 30 to 40 cm, where the depth is 0.25 mm with
- 1
operating voltage 80 to 350V. a resolution of 10 mm . IAM
Electro-luminescent displays have a very small mass and Ref.: Poole (1966), p.113; Bystrov (1985), p. 150.
thickness, they have good multiplexing capabilities, but at the An F-(scope) display is “a rectangular display in which a tar-
same time they are characterized by a number of shortcom- get appears as a centralized blip when the radar antenna is
ings: large dimensions and limited number of colors. IAM aimed at it. Horizontal and vertical aiming errors are respec-
Ref.: Poole (1966), Ch. 7; Fink (1982), p. 11.55; Bystrov (1985), p. 87. tively indicated by horizontal and vertical displacement of the
An elevation-range display uses rectangular sweep to record blip” (Fig. D49).
the position of the target in the elevation (vertical sweep) and Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 485.
range (horizontal sweep) coordinates. Its construction is anal- A G-(scope) display is a modified F-display in which wings
ogous to the azimuth-range display. To read the target alti- appear to grow on the blip, the width of the wings being
tude, lines of equal altitudes have been drawn on the inversely proportional to target range (Fig. D50). (Rare.)
transparent light filter in front of the display screen (CRT) in
Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 551.
the form of a hyperbola.
Basic shortcomings of the display: at great distances it is A gas-discharge display uses gas-discharge radiation. They
difficult to distinguish the lines of equal altitude from one operate in the glow discharge mode with a cold cathode at a
another, which leads to an increase in errors in reading the gas pressure of several hundred pascals and a voltage of 100
altitudes; a significant part of the usable space of the display to 200V. Monochrome and color displays with phosphor
is not used. To correct these shortcomings two scales are screens of the three primary colors are used. Structurally the
often used for range and elevation. This display is also called displays are in the form of gas-discharge panels (matrix dis-
an E-scope. IAM plays), forming a single unit with a great number of gas-dis-
charge cells controlled by direct or alternating high-frequency
Ref.: Barton (1964), p. 7; Druzhinin (1967), p. 411.
current. In the latter case, the effect of an internal memory is