Page 254 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 254
LOSS, in radar LOSS, in radar 244
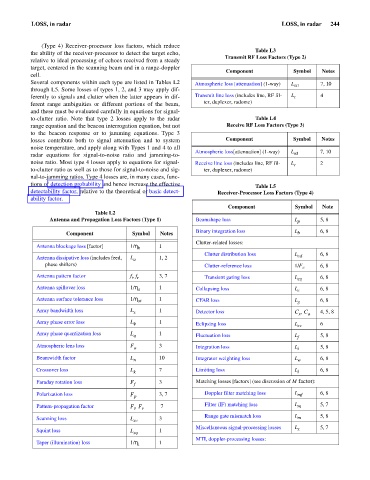
(Type 4) Receiver-processor loss factors, which reduce
Table L3
the ability of the receiver-processor to detect the target echo,
Transmit RF Loss Factors (Type 2)
relative to ideal processing of echoes received from a steady
target, centered in the scanning beam and in a range-doppler
Component Symbol Notes
cell.
Several components within each type are listed in Tables L2 Atmospheric loss [attenuation] (1-way) L a1 7, 10
through L5. Some losses of types 1, 2, and 3 may apply dif-
ferently to signals and clutter when the latter appears in dif- Transmit line loss (includes line, RF fil- L t 4
ferent range ambiguities or different portions of the beam, ter, duplexer, radome)
and these must be evaluated carefully in equations for signal-
to-clutter ratio. Note that type 2 losses apply to the radar Table L4
range equation and the beacon interrogation equation, but not Receive RF Loss Factors (Type 3)
to the beacon response or to jamming equations. Type 3
losses contribute both to signal attenuation and to system Component Symbol Notes
noise temperature, and apply along with Types 1 and 4 to all
Atmospheric loss[attenuation] (1-way) L a1 7, 10
radar equations for signal-to-noise ratio and jamming-to-
noise ratio. Most type 4 losses apply to equations for signal- Receive line loss (includes line, RF fil- L r 2
to-clutter ratio as well as to those for signal-to-noise and sig- ter, duplexer, radome)
nal-to-jamming ratios. Type 4 losses are, in many cases, func-
tions of detection probability and hence increase the effective Table L5
detectability factor, relative to the theoretical or basic detect- Receiver-Processor Loss Factors (Type 4)
ability factor.
Component Symbol Note
Table L2
Antenna and Propagation Loss Factors (Type 1) Beamshape loss L p 5, 8
Binary integration loss L 6, 8
Component Symbol Notes b
Clutter-related losses:
Antenna blockage loss [factor] 1/h b 1
Clutter distribution loss L 6, 8
Antenna dissipative loss (includes feed, L 1, 2 cd
a
phase shifters) Clutter-reference loss 1/F c 6, 8
Antenna pattern factor f , f 3, 7 Transient gating loss L eg 6, 8
t r
Antenna spillover loss 1/h s 1 Collapsing loss L c 6, 8
Antenna surface tolerance loss 1/h st 1 CFAR loss L g 6, 8
Array bandwidth loss L z 1 Detector loss C , C a 4, 5, 8
x
Array phase error loss L f 1 Eclipsing loss L ec 6
Array phase quantization loss L q 1 Fluctuation loss L f 5, 8
Atmospheric lens loss F a 3 Integration loss L i 5, 8
Beamwidth factor L n 10 Integrator weighting loss L w 6, 8
Crossover loss L k 7 Limiting loss L l 6, 8
Faraday rotation loss F f 3 Matching losses [factors] (see discussion of M factor):
Polarization loss F p 3, 7 Doppler filter matching loss L mf 6, 8
Pattern-propagation factor F , F r 7 Filter (IF) matching loss L m 5, 7
t
Range gate mismatch loss L 5, 8
Scanning loss L sc 3 m
Miscellaneous signal-processing losses L x 5, 7
Squint loss L sq 1
MTI, doppler-processing losses:
Taper (illumination) loss 1/h i 1