Page 272 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 272
magnetron, tunable mapping, sky object 262
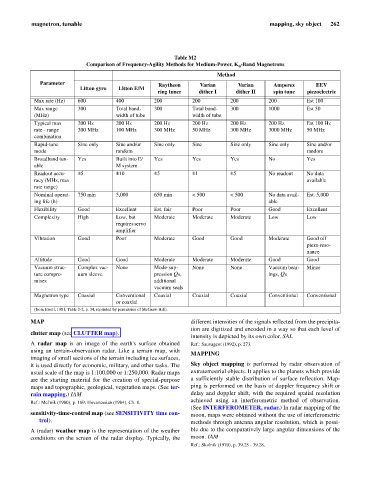
Table M2
Comparison of Frequency-Agility Methods for Medium-Power, K -Band Magnetrons
u
Method
Parameter Raytheon Varian Varian Amperex EEV
Litton gyro Litton E/M
ring tuner dither I dither II spin tune piezoelectric
Max rate (Hz) 600 400 200 200 200 200 Est 100
Max range 300 Total band- 300 Total band- 300 1000 Est 50
(MHz) width of tube width of tube
Typical max 200 Hz 200 Hz 200 Hz 200 Hz 200 Hz 200 Hz Est 100 Hz
rate - range 300 MHz 100 MHz 300 MHz 50 MHz 300 MHz 3000 MHz 50 MHz
combination
Rapid-tune Sine only Sine and/or Sine only Sine Sine only Sine only Sine and/or
mode random random
Broadband tun- Yes Built into E/ Yes Yes Yes No Yes
able M system
Readout accu- ±5 ±10 ±5 ±1 ±5 No readout No data
racy (MHz, max available
rate range)
Nominal operat- 750 min 5,000 650 min < 500 < 500 No data avail- Est. 5,000
ing life (h) able
Flexibility Good Excellent Est. fair Poor Poor Good Excellent
Complexity High Low, but Moderate Moderate Moderate Low Low
requires servo
amplifier
Vibration Good Poor Moderate Good Good Moderate Good off
piezo reso-
nance
Altitude Good Good Moderate Moderate Moderate Good Good
Vacuum struc- Complex vac- None Mode-sup- None None Vacuum bear- Minor
ture compro- uum sleeve pression Qs, ings, Qs
mises additional
vacuum seals
Magnetron type Coaxial Conventional Coaxial Coaxial Coaxial Conventional Conventional
or coaxial
(from Ewell, 1981, Table 2-2, p. 34, reprinted by permission of McGraw-Hill).
MAP different intensities of the signals reflected from the precipita-
tion are digitized and encoded in a way so that each level of
clutter map (see CLUTTER map).
intensity is depicted by its own color. SAL
A radar map is an image of the earth's surface obtained Ref.: Sauvageot (1992), p. 273.
using an terrain-observation radar. Like a terrain map, with
MAPPING
imaging of small sections of the terrain including ice surfaces,
it is used directly for economic, military, and other tasks. The Sky object mapping is performed by radar observation of
usual scale of the map is 1:100,000 or 1:250,000. Radar maps extraterrestrial objects. It applies to the planets which provide
are the starting material for the creation of special-purpose a sufficiently stable distribution of surface reflection. Map-
maps and topographic, geological, vegetation maps. (See ter- ping is performed on the basis of doppler frequency shift or
rain mapping.) IAM delay and doppler shift, with the required spatial resolution
achieved using an interferometric method of observation.
Ref.: Mel'nik (1980), p. 169; Hovanessian (1984), Ch. 8.
(See INTERFEROMETER, radar.) In radar mapping of the
sensitivity-time-control map (see SENSITIVITY time con- moon, maps were obtained without the use of interferometric
trol). methods through antenna angular resolution, which is possi-
A (radar) weather map is the representation of the weather ble due to the comparatively large angular dimensions of the
conditions on the screen of the radar display. Typically, the moon. IAM
Ref.: Skolnik (1970), p. 39.25 - 39.28.