Page 267 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 267
257 loss, scanning loss, weighting
The term scanning (pattern) loss has been used to denote where G is the ideal gain for uniform illumination, and effi-
0
beamshape loss (see Blake, 1980, p. 49), but that is an ciency factors for the feed, spillover, blockage, and antenna
entirely separate issue, not to be confused with the effect of tolerances are included along with illumination efficiency. If
the receiving beam not being directed toward the echoes from stated separately as a loss, the taper loss would be expressed
the preceding transmission. DKB as L = 1/h. DKB
i
ti
Ref.: Barton (1964), p. 150. Ref.: Barton (1969), App. A.
signal-processing loss (see miscellaneous signal-processing Transient gating loss in a doppler radar system using batch-
loss). processing results from the need to delay processing until
clutter with maximum observed range delay has entered the
The squint loss is the amount by which the gain is reduced
sample to be processed. Upon changing the beam position,
when the mainlobe is radiated at an angle other than the nor-
carrier frequency, or waveform, a clutter transient occurs,
mal to an array face, as in some frequency-sensitive
which lasts until clutter from the maximum range has entered
waveguide feeds. The beam is also described as being
the receiver. If the coherent dwell time is t and the maxi-
cd
squinted from the tracking axis in a conical-scanning radar,
mum range of significant clutter is R , corresponding to
mc
but in that case the loss is described as crossover loss). DKB
delay t = 2R /c, the transient gating loss is
mc
g
Ref.: Barton (1988), p. 150. t
cd
L = ----------------
eg t – t
cd g
DKB
Ref.: Barton (1988), p. 270.
Transmit [transmission-] line loss is the attenuation in the
RF components connecting the point at which transmitter
power is measured to the point at which antenna gain is mea-
sured. This loss may have components due to the waveguide
or coaxial line, the duplexer, rotating joints, directional cou-
plers for sampling the signal, and other RF devices through
which the signal must pass. It is entered as a separate loss
term in the standard radar equation and in the Blake chart.
DKB
tropospheric loss (see atmospheric loss).
Velocity response loss is the result of some targets signals
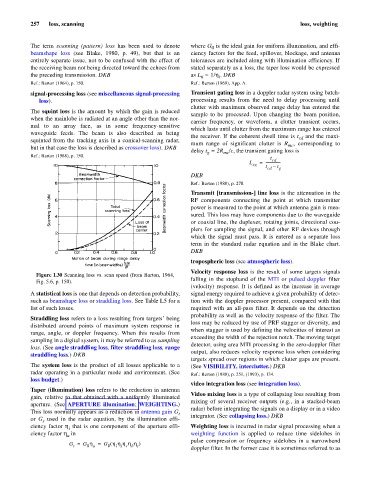
Figure L30 Scanning loss vs. scan speed (from Barton, 1964,
Fig. 5.6, p. 150). falling in the stopband of the MTI or pulsed doppler filter
(velocity) response. It is defined as the increase in average
A statistical loss is one that depends on detection probability, signal energy required to achieve a given probability of detec-
such as beamshape loss or straddling loss. See Table L5 for a tion with the doppler processor present, compared with that
list of such losses. required with an all-pass filter. It depends on the detection
probability as well as the velocity response of the filter. The
Straddling loss refers to a loss resulting from targets’ being
loss may be reduced by use of PRF stagger or diversity, and
distributed around points of maximum system response in
when stagger is used by defining the velocities of interest as
range, angle, or doppler frequency. When this results from
exceeding the width of the rejection notch. The moving target
sampling in a digital system, it may be referred to as sampling
detector, using area MTI processing in the zero-doppler filter
loss. (See angle straddling loss, filter straddling loss, range
output, also reduces velocity response loss when considering
straddling loss.) DKB
targets spread over regions in which clutter gaps are present.
The system loss is the product of all losses applicable to a (See VISIBILITY, interclutter.) DKB
radar operating in a particular mode and environment. (See Ref.: Barton (1988), p. 251, (1993), p. 134.
loss budget.)
video integration loss (see integration loss).
Taper (illumination) loss refers to the reduction in antenna
Video mixing loss is a type of collapsing loss resulting from
gain, relative to that obtained with a uniformly illuminated
mixing of several receiver outputs (e.g., in a stacked-beam
aperture. (See APERTURE illumination; WEIGHTING.)
radar) before integrating the signals on a display or in a video
This loss normally appears as a reduction in antenna gain G
t integrator. (See collapsing loss.) DKB
or G used in the radar equation, by the illumination effi-
r
ciency factor h that is one component of the aperture effi- Weighting loss is incurred in radar signal processing when a
i
ciency factor h in weighting function is applied to reduce time sidelobes in
a
pulse compression or frequency sidelobes in a narrowband
G = G h = G h h h h h( )
t 0 a 0 i f s b t
doppler filter. In the former case it is sometimes referred to as