Page 335 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 335
325 radar, aircraft tail-protection radar, airport surveillance (ASR)
narrow pulse (20 to 50 ns), narrow beam (0.25° to 0.4°), and
rapid scan rate (60 rpm or greater), with display ranges from
one to 5 km. The resolution is intended to be adequate to pro-
vide recognition of different classes of aircraft, as well as
resolving one aircraft from another as they stand in taxiways
at the end of an active runway. The radar must also detect and
display automobiles and trucks operating on or near taxiways.
Rain clutter presents a problem at the high microwave fre-
quencies used, and this is minimized by using a circularly
polarized antenna.
The newer generation of ASDEs used in the United
States is represented by the ASDE-3, the parameters of which
are listed in Table R1. DKB
IEEE (1993), p. 23; Skolnik (1988), pp. 116–126.
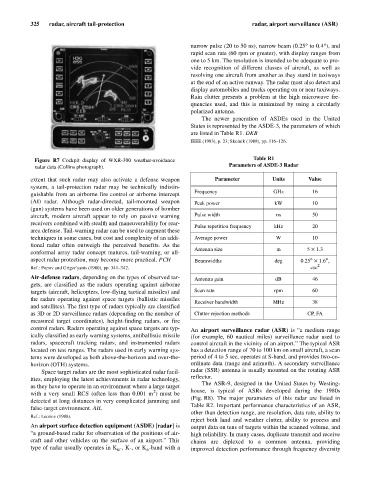
Figure R7 Cockpit display of WXR-300 weather-avoidance Table R1
radar data (Collins photograph). Parameters of ASDE-3 Radar
extent that such radar may also activate a defense weapon Parameter Units Value
system, a tail-protection radar may be technically indistin-
Frequency GHz 16
guishable from an airborne fire control or airborne intercept
(AI) radar. Although radar-directed, tail-mounted weapon Peak power kW 10
(gun) systems have been used on older generations of bomber
aircraft, modern aircraft appear to rely on passive warning Pulse width ns 50
receivers combined with stealth and maneuverability for rear-
Pulse repetition frequency kHz 20
area defense. Tail-warning radar can be used to augment these
techniques in some cases, but cost and complexity of an addi- Average power W 10
tional radar often outweigh the perceived benefits. As the
Antenna size m 5 ´ 1.3
conformal array radar concept matures, tail-warning, or all-
aspect radar protection, may become more practical. PCH Beamwidths deg 0.25° ´ ° ,
1.6
2
Ref.: Popov and Grigor'yants (1980), pp. 341–342. csc
Air-defense radars, depending on the types of observed tar- Antenna gain dB 46
gets, are classified as the radars operating against airborne
targets (aircraft, helicopters, low-flying tactical missiles) and Scan rate rpm 60
the radars operating against space targets (ballistic missiles
Receiver bandwidth MHz 38
and satellites). The first type of radars typically are classified
as 3D or 2D surveillance radars (depending on the number of Clutter rejection methods CP, FA
measured target coordinates), height-finding radars, or fire
control radars. Radars operating against space targets are typ- An airport surveillance radar (ASR) is “a medium-range
ically classified as early warning systems, antiballistic missile (for example, 60 nautical miles) surveillance radar used to
radars, spacecraft tracking radars, and instrumented radars control aircraft in the vicinity of an airport.” The typical ASR
located on test ranges. The radars used in early warning sys- has a detection range of 70 to 100 km on small aircraft, a scan
tems were developed as both above-the-horizon and over-the- period of 4 to 5 sec, operates at S-band, and provides two-co-
horizon (OTH) systems. ordinate data (range and azimuth). A secondary surveillance
Space target radars are the most sophisticated radar facil- radar (SSR) antenna is usually mounted on the rotating ASR
reflector.
ities, employing the latest achievements in radar technology,
The ASR-9, designed in the United States by Westing-
as they have to operate in an environment where a large target
2
with a very small RCS (often less than 0.001 m ) must be house, is typical of ASRs developed during the 1980s
(Fig. R8). The major parameters of this radar are listed in
detected at long distances in very complicated jamming and
Table R2. Important performance characteristics of an ASR,
false-target environment. AIL
other than detection range, are resolution, data rate, ability to
Ref.: Leonov (1988).
reject both land and weather clutter, ability to process and
An airport surface detection equipment (ASDE) [radar] is output data on tens of targets within the scanned volume, and
“a ground-based radar for observation of the positions of air- high reliability. In many cases, duplicate transmit and receive
craft and other vehicles on the surface of an airport.” This chains are diplexed to a common antenna, providing
type of radar usually operates in K -, K-, or K -band with a improved detection performance through frequency diversity
a
u